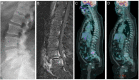
Disappearance of FDG uptake on PET scan after antimicrobial therapy could help for the diagnosis of Coxiella burnetii spondylodiscitis
- PMID: 27015880
- PMCID: PMC4823539
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2015-214008
Disappearance of FDG uptake on PET scan after antimicrobial therapy could help for the diagnosis of Coxiella burnetii spondylodiscitis
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
