Comparison of Modified Blumgart pancreaticojejunostomy and pancreaticogastrostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy
- PMID: 27017162
- PMCID: PMC4814607
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2015.09.007
Comparison of Modified Blumgart pancreaticojejunostomy and pancreaticogastrostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy
Abstract
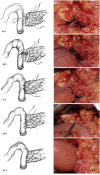
Background: The aim of this study was to compare perioperative outcomes after Blumgart pancreaticojejunostomy (PJ) and pancreaticogastrostomy (PG) for pancreatic-enteric reconstruction following pancreaticoduodenectomy.
Methods: Data of patients undergoing Blumgart PJ and PG were retrieved from prospectively-collected database. Matched patients in each surgical groups were included based on the Callery risk scoring system for clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula (CR-POPF) (grades B and C). Surgical parameters and risks were compared between these two groups.
Results: A total of 206 patients undergoing PD were included. Blumgart PJ was associated with shorter postoperative hospital stay (median (range) 25 (10-99) vs. 27 (10-97) days, P = 0.022). There was no surgical mortality in the Blumgart PJ group, but a 4.9% perioperative mortality in the PG, P = 0.030. The CR-POPF by Blumgrt PG is significantly lower than that by PG for overall patients (7% vs. 20%, P = 0.007), especially for those in intermediate fistula risk zone (6% vs. 21%, P =0.048) and high fistula risk zone (14% vs. 47%, P=0.038).
Conclusions: Blumgart PJ is superior to PG in terms of pancreatic leakage and surgical mortality. Blumgart PJ can be recommended for pancreatic reconstruction after PD for all pancreatic remnant subtypes.
Copyright © 2015 International Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association Inc. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pancreaticojejunostomy vs. pancreaticogastrostomy following pancreaticoduodenectomy: results of comparative study.Minerva Chir. 2011 Aug;66(4):295-302. Minerva Chir. 2011. PMID: 21873963
-
Outcomes comparing a pancreaticogastrostomy (PG) and a pancreaticojejunostomy (PJ) after a pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD).HPB (Oxford). 2011 Oct;13(10):723-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2011.00363.x. HPB (Oxford). 2011. PMID: 21929673 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between pancreaticojejunostomy and pancreaticogastrostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy.J Formos Med Assoc. 2007 Sep;106(9):717-27. doi: 10.1016/S0929-6646(08)60033-9. J Formos Med Assoc. 2007. PMID: 17908661
-
Pancreaticogastrostomy has advantages over pancreaticojejunostomy on pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Int J Surg. 2016 Dec;36(Pt A):18-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.10.020. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Int J Surg. 2016. PMID: 27768898
-
Meta-analysis of pancreaticogastrostomy versus pancreaticojejunostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy.Br J Surg. 2014 Sep;101(10):1196-208. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9553. Epub 2014 Jul 16. Br J Surg. 2014. PMID: 25042895 Review.
Cited by
-
Technical Details and Results of a Modified End-to-Side Technique of Pancreatojejunostomy: a Personal Series of 100 Patients.J Gastrointest Surg. 2017 Dec;21(12):2090-2099. doi: 10.1007/s11605-017-3587-7. Epub 2017 Sep 21. J Gastrointest Surg. 2017. PMID: 28936588
-
Pancreaticojejunostomy With Externalized Stent vs Pancreaticogastrostomy With Externalized Stent for Patients With High-Risk Pancreatic Anastomosis: A Single-Center, Phase 3, Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Surg. 2020 Apr 1;155(4):313-321. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.6035. JAMA Surg. 2020. PMID: 32101272 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Initial Experience of Consecutive Robotic Pancreatoduodenectomies With Patient Reported Outcomes From a Single Center in the UK.J Clin Med Res. 2021 Aug;13(8):435-437. doi: 10.14740/jocmr4574. Epub 2021 Aug 30. J Clin Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34527100 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic head cancer and periampullary lesions.Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2021 Mar 28;5(5):589-596. doi: 10.1002/ags3.12457. eCollection 2021 Sep. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2021. PMID: 34585043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Obesity on Perioperative Outcomes in Robotic Pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Propensity Score-Matched Study.Int J Med Robot. 2024 Dec;20(6):e70034. doi: 10.1002/rcs.70034. Int J Med Robot. 2024. PMID: 39698987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kleespies A., Rentsch M., Seeliger H., Albertsmeier M., Jauch K.W., Bruns C.J. Blumgart anastomosis for pancreaticojejunostomy minimizes severe complications after pancreatic head resection. Br J Surg. 2009;96:741–750. - PubMed
-
- Fujii T., Sugimoto H., Yamada S., Kanda M., Suenaga M., Takami H. Modified Blumgart anastomosis for pancreaticojejunostomy: technical improvement in matched historical control study. J Gastrointest Surg. 2014;18:1108–1115. - PubMed
-
- Kleespies A., Albertsmeier M., Obeidat F., Seeliger H., Jauch K.W., Bruns C.J. The challenge of pancreatic anastomosis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2008;393:459–471. - PubMed
-
- Grobmyer S.R., Kooby D., Blumgart L.H., Hochwald S.N. Novel pancreaticojejunostomy with a low rate of anastomotic failure-related complications. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;210:54–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

