Enhanced Dopamine Release by Dopamine Transport Inhibitors Described by a Restricted Diffusion Model and Fast-Scan Cyclic Voltammetry
- PMID: 27018734
- PMCID: PMC4909544
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00277
Enhanced Dopamine Release by Dopamine Transport Inhibitors Described by a Restricted Diffusion Model and Fast-Scan Cyclic Voltammetry
Abstract
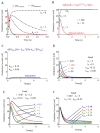
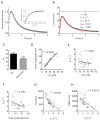
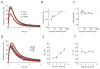
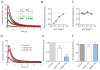
Fast-scan cyclic voltammetry (FSCV) using carbon fiber electrodes is widely used to rapidly monitor changes in dopamine (DA) levels in vitro and in vivo. Current analytical approaches utilize parameters such as peak oxidation current amplitude and decay times to estimate release and uptake processes, respectively. However, peak amplitude changes are often observed with uptake inhibitors, thereby confounding the interpretation of these parameters. To overcome this limitation, we demonstrate that a simple five-parameter, two-compartment model mathematically describes DA signals as a balance of release (r/ke) and uptake (ku), summed with adsorption (kads and kdes) of DA to the carbon electrode surface. Using nonlinear regression, we demonstrate that our model precisely describes measured DA signals obtained in brain slice recordings. The parameters extracted from these curves were then validated using pharmacological manipulations that selectively alter vesicular release or DA transporter (DAT)-mediated uptake. Manipulation of DA release through altering the Ca(2+)/Mg(2+) ratio or adding tetrodotoxin reduced the release parameter with no effect on the uptake parameter. DAT inhibitors methylenedioxypyrovalerone, cocaine, and nomifensine significantly reduced uptake and increased vesicular DA release. In contrast, a low concentration of amphetamine reduced uptake but had no effect on DA release. Finally, the kappa opioid receptor agonist U50,488 significantly reduced vesicular DA release but had no effect on uptake. Together, these data demonstrate a novel analytical approach to distinguish the effects of manipulations on DA release or uptake that can be used to interpret FSCV data.
Keywords: Voltammetry; brain slice; cathinones; dopamine transporter; drug abuse; kinetics.
Figures

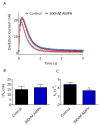
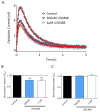
References
-
- Wightman RM, Zimmerman JB. Control of dopamine extracellular concentration in rat striatum by impulse flow and uptake. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1990;15:135–144. - PubMed
-
- Jones SR, Garris PA, Kilts CD, Wightman RM. Comparison of dopamine uptake in the basolateral amygdaloid nucleus, caudate-putamen, and nucleus accumbens of the rat. J Neurochem. 1995;64:2581–2589. - PubMed
-
- Wu Q, Reith ME, Wightman RM, Kawagoe KT, Garris PA. Determination of release and uptake parameters from electrically evoked dopamine dynamics measured by real-time voltammetry. J Neurosci Methods. 2001;112:119–133. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

