BN-9, a chimeric peptide with mixed opioid and neuropeptide FF receptor agonistic properties, produces nontolerance-forming antinociception in mice
- PMID: 27018797
- PMCID: PMC4867745
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13489
BN-9, a chimeric peptide with mixed opioid and neuropeptide FF receptor agonistic properties, produces nontolerance-forming antinociception in mice
Abstract
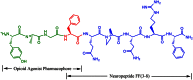
Background and purpose: Neuropeptide FF (NPFF) behaves as an endogenous opioid-modulating peptide. In the present study, the opioid and NPFF pharmacophore-containing chimeric peptide BN-9 was synthesized and pharmacologically characterized.
Experimental approach: Agonist activities of BN-9 at opioid and NPFF receptors were characterized in in vitro cAMP assays. Antinociceptive activities of BN-9 were evaluated in the mouse tail-flick and formalin tests. Furthermore, its side effects were investigated in rotarod, antinociceptive tolerance, reward and gastrointestinal transit tests.
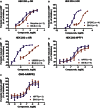
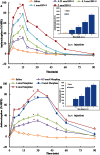
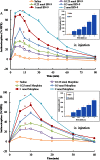
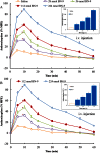
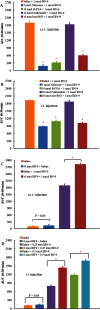
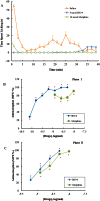
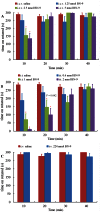
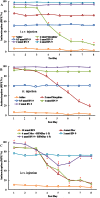
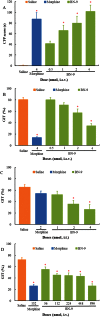
Key results: BN-9 acted as a novel multifunctional agonist at μ, δ, κ, NPFF1 and NPFF2 receptors in cAMP assays. In the tail-flick test, BN-9 produced dose-related antinociception and was approximately equipotent to morphine; this antinociception was blocked by μ and κ receptor antagonists, but not by the δ receptor antagonist. In the formalin test, supraspinal administration of BN-9 produced significant analgesia. Notably, repeated administration of BN-9 produced analgesia without loss of potency over 8 days. In contrast, repeated i.c.v. co-administration of BN-9 with the NPFF receptor antagonist RF9 produced significant antinociceptive tolerance. Furthermore, i.c.v. BN-9 induced conditioned place preference. When given by the same routes, BN-9 had a more than eightfold higher ED50 value for gastrointestinal transit inhibition compared with the ED50 values for antinociception.
Conclusions and implications: BN-9 produced a robust, nontolerance-forming analgesia with limited inhibition of gastrointestinal transit. As BN-9 is able to activate both opioid and NPFF systems, this provides an interesting approach for the development of novel analgesics with minimal side effects.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological characterization of EN-9, a novel chimeric peptide of endomorphin-2 and neuropeptide FF that produces potent antinociceptive activity and limited tolerance.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Sep;108:364-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.03.017. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26970017
-
Systemic administration of the bifunctional opioid/neuropeptide FF receptors agonist BN-9 produced peripheral antinociception in preclinical mouse models of pain.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Oct 15;837:53-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.08.039. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30172787
-
Structure-Based Optimization of Multifunctional Agonists for Opioid and Neuropeptide FF Receptors with Potent Nontolerance Forming Analgesic Activities.J Med Chem. 2016 Nov 23;59(22):10198-10208. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01181. Epub 2016 Nov 11. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27798836
-
The antinociceptive properties of endomorphin-1 and endomorphin-2 in the mouse.Jpn J Pharmacol. 2002 Jul;89(3):216-20. doi: 10.1254/jjp.89.216. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12184724 Review.
-
Nonpeptide ligands of neuropeptide FF: current status and structural insights.Future Med Chem. 2012 Jun;4(9):1085-92. doi: 10.4155/fmc.12.67. Future Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22709252 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heteromerization of μ-opioid receptor and cholecystokinin B receptor through the third transmembrane domain of the μ-opioid receptor contributes to the anti-opioid effects of cholecystokinin octapeptide.Exp Mol Med. 2018 May 21;50(5):1-16. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0090-5. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29780163 Free PMC article.
-
Orai1 Plays a Crucial Role in Central Sensitization by Modulating Neuronal Excitability.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 24;38(4):887-900. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3007-17.2017. Epub 2017 Dec 11. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29229703 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of First-in-Class Peptidomimetic Neurolysin Activators Possessing Enhanced Brain Penetration and Stability.J Med Chem. 2021 Sep 9;64(17):12705-12722. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00759. Epub 2021 Aug 26. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34436882 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Opioid-Neuropeptide FF Small Molecule Ligands Demonstrate Analgesia with Reduced Tolerance Liabilities.Molecules. 2025 Jul 3;30(13):2851. doi: 10.3390/molecules30132851. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40649365 Free PMC article.
-
GpTx-1 and [Ala5 , Phe6 , Leu26 , Arg28 ]GpTx-1, two peptide NaV 1.7 inhibitors: analgesic and tolerance properties at the spinal level.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Oct;175(20):3911-3927. doi: 10.1111/bph.14461. Epub 2018 Sep 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30076786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altier N, Dray A, Menard D, Henry JL (2000). Neuropeptide FF attenuates allodynia in models of chronic inflammation and neuropathy following intrathecal or intracerebroventricular administration. Eur J Pharmacol 407: 245–255. - PubMed
-
- Ballet S, Pietsch M, Abell AD (2008). Multiple ligands in opioid research. Protein Pept Lett 15: 668–682. - PubMed
-
- Bonini JA, Jones KA, Adham N, Forray C, Artymyshyn R, Durkin MM et al. (2000). Identification and characterization of two G protein‐coupled receptors for neuropeptide FF. J Biol Chem 275: 39324–39331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

