Essential biphasic role for JAK3 catalytic activity in IL-2 receptor signaling
- PMID: 27018889
- PMCID: PMC4837022
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.2056
Essential biphasic role for JAK3 catalytic activity in IL-2 receptor signaling
Abstract
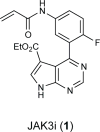
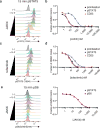
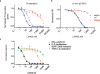
To drive lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation, common γ-chain (γc) cytokine receptors require hours to days of sustained stimulation. JAK1 and JAK3 kinases are found together in all γc-receptor complexes, but how their respective catalytic activities contribute to signaling over time is not known. Here we dissect the temporal requirements for JAK3 kinase activity with a selective covalent inhibitor (JAK3i). By monitoring phosphorylation of the transcription factor STAT5 over 20 h in CD4(+) T cells stimulated with interleukin 2 (IL-2), we document a second wave of signaling that is much more sensitive to JAK3i than the first wave. Selective inhibition of this second wave is sufficient to block cyclin expression and entry to S phase. An inhibitor-resistant JAK3 mutant (C905S) rescued all effects of JAK3i in isolated T cells and in mice. Our chemical genetic toolkit elucidates a biphasic requirement for JAK3 kinase activity in IL-2-driven T cell proliferation and will find broad utility in studies of γc-receptor signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
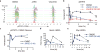
Comment in
-
Immunology: JAK3 inhibition—is it sufficient?Nat Chem Biol. 2016 May;12(5):308-10. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2066. Nat Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27556128 No abstract available.
References
-
- Miyazaki T, et al. Functional activation of Jak1 and Jak3 by selective association with IL-2 receptor subunits. Science. 1994;266:1045–1047. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

