MicroRNA-20a-5p contributes to hepatic glycogen synthesis through targeting p63 to regulate p53 and PTEN expression
- PMID: 27019188
- PMCID: PMC4956936
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12835
MicroRNA-20a-5p contributes to hepatic glycogen synthesis through targeting p63 to regulate p53 and PTEN expression
Abstract
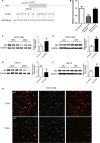
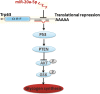
Recently, it is implicated that aberrant expression of microRNAs (miRs) is associated with insulin resistance. However, the role of miR-17 family in hepatic insulin resistance and its underlying mechanisms remain unknown. In this study, we provided mechanistic insight into the effects of miR-20a-5p, a member of miR-17 family, on the regulation of AKT/GSK pathway and glycogenesis in hepatocytes. MiR-20a-5p was down-regulated in the liver of db/db mice, and NCTC1469 cells and Hep1-6 cells treated with high glucose, accompanied by reduced glycogen content and impaired insulin signalling. Notably, inhibition of miR-20a-5p significantly reduced glycogen synthesis and AKT/GSK activation, whereas overexpression of miR-20a-5p led to elevated glycogenesis and activated AKT/GSK signalling pathway. In addition, miR-20a-5p mimic could reverse high glucose-induced impaired glycogenesis and AKT/GSK activation in NCTC1469 and Hep1-6 cells. P63 was identified as a target of miR-20a-5p by bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay. Knockdown of p63 in the NCTC1469 cells and the Hep1-6 cells by transfecting with siRNA targeting p63 could increase glycogen content and reverse miR-20a-5p inhibition-induced reduced glycogenesis and activation of AKT and GSK, suggesting that p63 participated in miR-20a-5p-mediated glycogenesis in hepatocytes. Moreover, our results indicate that p63 might directly bind to p53, thereby regulating PTEN expression and in turn participating in glycogenesis. In conclusion, we found novel evidence suggesting that as a member of miR-17 family, miR-20a-5p contributes to hepatic glycogen synthesis through targeting p63 to regulate p53 and PTEN expression.
Keywords: PTEN; glycogen synthesis; miR-20a-5p; p53; p63.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hepatic miR-181b-5p Contributes to Glycogen Synthesis Through Targeting EGR1.Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Jun;64(6):1548-1559. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5442-4. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Dig Dis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30627917
-
MiR-301a mediates the effect of IL-6 on the AKT/GSK pathway and hepatic glycogenesis by regulating PTEN expression.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(4):1413-24. doi: 10.1159/000373962. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25790935
-
MicroRNA 152 regulates hepatic glycogenesis by targeting PTEN.FEBS J. 2016 May;283(10):1935-46. doi: 10.1111/febs.13713. Epub 2016 Apr 2. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26996529
-
How MicroRNAs Command the Battle against Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 28;25(11):5865. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115865. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory mechanism of miR-20a-5p expression in Cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2022 May 16;8(1):262. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01005-5. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35577802 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uncarboxylated osteocalcin alleviates the inhibitory effect of high glucose on osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating TP63.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Apr 27;22(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12860-021-00365-7. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33906607 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts drive colorectal cancer cell progression through exosomal miR-20a-5p-mediated targeting of PTEN and stimulating interleukin-6 production.BMC Cancer. 2024 Apr 1;24(1):400. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12190-0. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38561726 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles promote liver regeneration via miR-20a-5p/PTEN.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 25;14:1168545. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1168545. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37305542 Free PMC article.
-
Unique circulating microRNA associations with dysglycemia in people living with HIV and alcohol use.Physiol Genomics. 2022 Jan 1;54(1):36-44. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00085.2021. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Physiol Genomics. 2022. PMID: 34859690 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Role of PTEN in Insulin Signaling and Resistance.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020 Aug 3;10(8):a036137. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a036137. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020. PMID: 31964643 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004; 116: 281–97. - PubMed
-
- Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, et al Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013; 495: 384–8. - PubMed
-
- He A, Zhu L, Gupta N, et al Overexpression of micro ribonucleic acid 29, highly up‐regulated in diabetic rats, leads to insulin resistance in 3T3‐L1 adipocytes. Mol Endocrinol. 2007; 21: 2785–94. - PubMed
-
- Trajkovski M, Hausser J, Soutschek J, et al MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity. Nature. 2011; 474: 649–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

