Deep sequencing leads to the identification of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A as a key element in Rsv1-mediated lethal systemic hypersensitive response to Soybean mosaic virus infection in soybean
- PMID: 27019403
- PMCID: PMC6638201
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12407
Deep sequencing leads to the identification of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A as a key element in Rsv1-mediated lethal systemic hypersensitive response to Soybean mosaic virus infection in soybean
Abstract
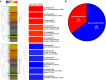
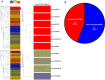
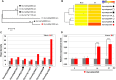
Rsv1, a single dominant resistance locus in soybean, confers extreme resistance to the majority of Soybean mosaic virus (SMV) strains, but is susceptible to the G7 strain. In Rsv1-genotype soybean, G7 infection provokes a lethal systemic hypersensitive response (LSHR), a delayed host defence response. The Rsv1-mediated LSHR signalling pathway remains largely unknown. In this study, we employed a genome-wide investigation to gain an insight into the molecular interplay between SMV G7 and Rsv1-genotype soybean. Small RNA (sRNA), degradome and transcriptome sequencing analyses were used to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and microRNAs (DEMs) in response to G7 infection. A number of DEGs, DEMs and microRNA targets, and the interaction network of DEMs and their target mRNAs responsive to G7 infection, were identified. Knock-down of one of the identified DEGs, the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A), diminished the LSHR and enhanced viral accumulation, suggesting the essential role of eIF5A in the G7-induced, Rsv1-mediated LSHR signalling pathway. This work provides an in-depth genome-wide analysis of high-throughput sequencing data, and identifies multiple genes and microRNA signatures that are associated with the Rsv1-mediated LSHR.
Keywords: Soybean mosaic virus; degradome-seq; eukaryotic translation initiation factor; lethal systemic hypersensitive response; sRNA-seq; transcriptome-seq; virus-host interaction.
© 2016 HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN IN RIGHT OF CANADA MOLECULAR PLANT PATHOLOGY © 2016 BSPP AND JOHN WILEY & SONS LTD.
Figures




References
-
- Annamalai, P. and Rao, A.L. (2005) Replication‐independent expression of genome components and capsid protein of Brome mosaic virus in planta: a functional role for viral replicase in RNA packaging. Virology 338, 96–111. - PubMed
-
- Babu, M. , Gagarinova, A.G. , Brandle, J.E. and Wang, A. (2008) Association of the transcriptional response of soybean plants with Soybean mosaic virus systemic infection. J. Gen. Virol. 89, 1069–1080. - PubMed
-
- Baulcombe, D. (2004) RNA silencing in plants. Nature, 431, 356–363. - PubMed
-
- Bilgin, D.D. , Aldea, M. , O'Neill, B.F. , Benitez, M. , Li, M. , Clough, S.J. and DeLucia, E.H. (2008) Elevated ozone alters soybean–virus interaction. Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 21, 1297–1308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

