GD2-specific CAR T Cells Undergo Potent Activation and Deletion Following Antigen Encounter but can be Protected From Activation-induced Cell Death by PD-1 Blockade
- PMID: 27019998
- PMCID: PMC4923328
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2016.63
GD2-specific CAR T Cells Undergo Potent Activation and Deletion Following Antigen Encounter but can be Protected From Activation-induced Cell Death by PD-1 Blockade
Abstract
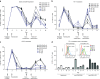
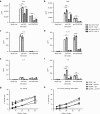
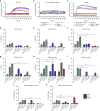
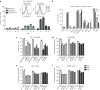
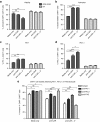
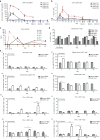
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells have shown great promise in the treatment of hematologic malignancies but more variable results in the treatment of solid tumors and the persistence and expansion of CAR T cells within patients has been identified as a key correlate of antitumor efficacy. Lack of immunological "space", functional exhaustion, and deletion have all been proposed as mechanisms that hamper CAR T-cell persistence. Here we describe the events following activation of third-generation CAR T cells specific for GD2. CAR T cells had highly potent immediate effector functions without evidence of functional exhaustion in vitro, although reduced cytokine production reversible by PD-1 blockade was observed after longer-term culture. Significant activation-induced cell death (AICD) of CAR T cells was observed after repeated antigen stimulation, and PD-1 blockade enhanced both CAR T-cell survival and promoted killing of PD-L1(+) tumor cell lines. Finally, we assessed CAR T-cell persistence in patients enrolled in the CARPETS phase 1 clinical trial of GD2-specific CAR T cells in the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Together, these data suggest that deletion also occurs in vivo and that PD-1-targeted combination therapy approaches may be useful to augment CAR T-cell efficacy and persistence in patients.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

