CO2-breathing and piercing polymersomes as tunable and reversible nanocarriers
- PMID: 27020003
- PMCID: PMC4810324
- DOI: 10.1038/srep23624
CO2-breathing and piercing polymersomes as tunable and reversible nanocarriers
Abstract
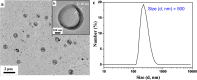
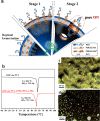
Despite numerous studies on utilizing polymeric vesicles as nanocapsules, fabrication of tunable molecular pathways on transportable vesicle walls remains challenging. Traditional methods for building penetrated channels on vesicular membrane surface often involve regulating the solvent polarity or photo-cross-linking. Herein, we developed a neat, green approach of stimulation by using CO2 gas as "molecular drill" to pierce macroporous structures on the membrane of polymersomes. By simply introducing CO2/N2 gases into the aqueous solution of self-assemblies without accumulating any byproducts, we observed two processes of polymeric shape transformation: "gas breathing" and "gas piercing." Moreover, the pathways in terms of dimension and time were found to be adjustable simply by controlling the CO2 stimulation level for different functional encapsulated molecules in accumulation, transport, and releasing. CO2-breathing and piercing of polymersomes offers a promising functionality to tune nanocapsules for encapsulating and releasing fluorescent dyes and bioactive molecules in living systems and also a unique platform to mimic the structural formation of nucleus pore complex and the breathing process in human beings and animals.
Figures




References
-
- Discher D. E. & Eisenberg A. Polymer vesicles. Science 297, 967–973 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Blanazs A., Armes S. P. & Ryan A. J. Self-assembled block copolymer aggregates: from micelles to vesicles and their biological applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 30, 267–277 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Du J. & O’Reilly R. K. Advances and challenges in smart and functional polymer vesicles. Soft Matter 5, 3544–3561 (2009).
-
- Li M. & Keller P. Stimuli-responsive polymer vesicles. Soft Matter 5, 927–937 (2009).
-
- LoPresti C., Lomas H., Massignani M., Smart T. & Battaglia G. Polymersomes: nature inspired nanometer sized compartments. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 3576–3590 (2009).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

