Gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection using sodium carboxymethylcellulose as a new injection substance
- PMID: 27020144
- PMCID: PMC5131580
- DOI: 10.5387/fms.2015-27
Gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection using sodium carboxymethylcellulose as a new injection substance
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the feasibility of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) using sodium carboxymethylcellulose (SCMC) for gastric cancer.
Methods: During October 2011 through April 2013, 98 lesions from 98 patients who underwent ESD using SCMC (ESD-SCMC) for early gastric cancer were enrolled in this study. Two endoscopists, who had each performed fewer than 30 ESD procedures (less-experienced ESD physicians), performed ESD-SCMC under the supervision of two experts. The primary outcome was the en bloc resection rate. Secondary outcomes included the complete resection rate, the procedural time, the bleeding rate after SCMC injection, and complications. Patient characteristics, time necessary for hemostasis after SCMC injection, rate of treatment completion by less-experienced ESD physicians alone, and the effects of SCMC during ESD and on resected specimens were also evaluated.
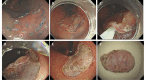
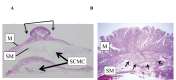
Results: The en bloc resection rate was 100%. Among these resections, 87.8% of the cases were completed by a less-experienced ESD physician alone. The complete resection rate was 98.0%. The mean total procedural time was 75.4 min. The mean incidence of intraoperative bleeding following SCMC local injection was 1.7 times. No bleeding was observed after SCMC injection in 29.6% of cases (29/98). Five complications occurred: one case of microperforation (1.0%) and four cases of postoperative bleeding (4.0%). SCMC remained in the submucosa. The submucosa was readily manipulated when the deep submucosa was dissected, even after placing the specimen on a slide.
Conclusion: ESD-SCMC is feasible for the resection of early gastric cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel method of endoscopic submucosal dissection with blunt abrasion by submucosal injection of sodium carboxymethylcellulose: an animal preliminary study.Gastrointest Endosc. 2006 Dec;64(6):958-65. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2006.07.035. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006. PMID: 17140905
-
Efficacy of Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose Compared to Sodium Hyaluronate as Submucosal Injectant for Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Digestion. 2021;102(5):753-759. doi: 10.1159/000513148. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Digestion. 2021. PMID: 33611330 Clinical Trial.
-
Implementation of endoscopic submucosal dissection in a country with a low incidence of gastric cancer: Results from a prospective national registry.United European Gastroenterol J. 2021 Jul;9(6):718-726. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12101. Epub 2021 Jun 2. United European Gastroenterol J. 2021. PMID: 34077636 Free PMC article.
-
Updated evaluation of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus surgery for early gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2020 Jan;73:28-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.11.027. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Int J Surg. 2020. PMID: 31783166
-
AGA Institute Clinical Practice Update: Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in the United States.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jan;17(1):16-25.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.07.041. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30077787 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevention of Stricture after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Superficial Esophageal Cancer: A Review of the Literature.J Clin Med. 2020 Dec 23;10(1):20. doi: 10.3390/jcm10010020. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33374780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Polymeric Formulation for Removal of Gastrointestinal Polyps by Digestive Endoscopy.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Apr 2;12(4):322. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12040322. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32252471 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of temperature-response collagen-genipin sols as a novel submucosal injection material for endoscopic resection.Endosc Int Open. 2019 Apr;7(4):E561-E567. doi: 10.1055/a-0867-9450. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Endosc Int Open. 2019. PMID: 30957006 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Submucosal Fibrosis and Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of Recurrent Esophageal Squamous Cell Cancers after Chemoradiotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 26;14(19):4685. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194685. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gotoda T, Kondo H, Ono H, et al. A new endoscopic mucosal resection procedure using an insulation-tipped electrosurgical knife for rectal flat lesions:report of two cases. Gastrointest Endosc, 50: 560-563, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Ohkuwa M, Hosokawa K, Boku N, Ohtu H, Tajiri H, Yoshida S. New endoscopic treatment for intramucosal gastric tumors using an insulated-tip diathermic knife. Endoscopy, 33: 221-226, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Rosch T, Sarbia M, Schumacher B, et al. Attempted endoscopic en bloc resection of mucosal and submucosal tumors using insulated-tip knives:A pilot series. Endoscopy, 36: 788-801, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Oyama T, Kikuchi Y. Aggressive endoscopic mucosal resection in the upper GI tract─Hook knife EMR method. Min Invas Ther Allied Technol, 11: 291-295, 2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

