Meta-analysis of gene-environment-wide association scans accounting for education level identifies additional loci for refractive error
- PMID: 27020472
- PMCID: PMC4820539
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11008
Meta-analysis of gene-environment-wide association scans accounting for education level identifies additional loci for refractive error
Abstract
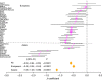
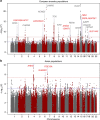
Myopia is the most common human eye disorder and it results from complex genetic and environmental causes. The rapidly increasing prevalence of myopia poses a major public health challenge. Here, the CREAM consortium performs a joint meta-analysis to test single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) main effects and SNP × education interaction effects on refractive error in 40,036 adults from 25 studies of European ancestry and 10,315 adults from 9 studies of Asian ancestry. In European ancestry individuals, we identify six novel loci (FAM150B-ACP1, LINC00340, FBN1, DIS3L-MAP2K1, ARID2-SNAT1 and SLC14A2) associated with refractive error. In Asian populations, three genome-wide significant loci AREG, GABRR1 and PDE10A also exhibit strong interactions with education (P<8.5 × 10(-5)), whereas the interactions are less evident in Europeans. The discovery of these loci represents an important advance in understanding how gene and environment interactions contribute to the heterogeneity of myopia.
Figures
References
-
- Morgan I. G., Ohno-Matsui K. & Saw S. M. Myopia. Lancet 379, 1739–1748 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Saw S. M., Gazzard G., Shih-Yen E. C. & Chua W. H. Myopia and associated pathological complications. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 25, 381–391 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Sanfilippo P. G., Hewitt A. W., Hammond C. J. & Mackey D. A. The heritability of ocular traits. Surv. Ophthalmol. 55, 561–583 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Wong T. Y. et al. Prevalence and risk factors for refractive errors in adult Chinese in Singapore. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 41, 2486–2494 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MR/K023721/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K08 EY022943/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY024233/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- 102215/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 EY014685/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K006584/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SRF/01/010/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N003284/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/3/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/4/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

