Highly Dynamic and Specific Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate, Septin, and Cell Wall Integrity Pathway Responses Correlate with Caspofungin Activity against Candida albicans
- PMID: 27021331
- PMCID: PMC4879351
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02711-15
Highly Dynamic and Specific Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate, Septin, and Cell Wall Integrity Pathway Responses Correlate with Caspofungin Activity against Candida albicans
Abstract
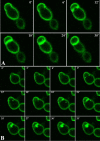
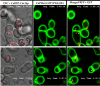
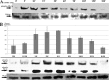
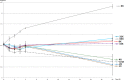
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P2] activates the yeast cell wall integrity pathway. Candida albicans exposure to caspofungin results in the rapid redistribution of PI(4,5)P2 and septins to plasma membrane foci and subsequent fungicidal effects. We studied C. albicans PI(4,5)P2 and septin dynamics and protein kinase C (PKC)-Mkc1 cell wall integrity pathway activation following exposure to caspofungin and other drugs. PI(4,5)P2 and septins were visualized by live imaging of C. albicans cells coexpressing green fluorescent protein (GFP)-pleckstrin homology (PH) domain and red fluorescent protein-Cdc10p, respectively. PI(4,5)P2 was also visualized in GFP-PH domain-expressing C. albicans mkc1 mutants. Mkc1p phosphorylation was measured as a marker of PKC-Mkc1 pathway activation. Fungicidal activity was assessed using 20-h time-kill assays. Caspofungin immediately induced PI(4,5)P2 and Cdc10p colocalization to aberrant foci, a process that was highly dynamic over 3 h. PI(4,5)P2 levels increased in a dose-response manner at caspofungin concentrations of ≤4× MIC and progressively decreased at concentrations of ≥8× MIC. Caspofungin exposure resulted in broad-based mother-daughter bud necks and arrested septum-like structures, in which PI(4,5)P2 and Cdc10 colocalized. PKC-Mkc1 pathway activation was maximal within 10 min, peaked in response to caspofungin at 4× MIC, and declined at higher concentrations. The caspofungin-induced PI(4,5)P2 redistribution remained apparent in mkc1 mutants. Caspofungin exerted dose-dependent killing and paradoxical effects at ≤4× and ≥8× MIC, respectively. Fluconazole, amphotericin B, calcofluor white, and H2O2 did not impact the PI(4,5)P2 or Cdc10p distribution like caspofungin did. Caspofungin exerts rapid PI(4,5)P2-septin and PKC-Mkc1 responses that correlate with the extent of C. albicans killing, and the responses are not induced by other antifungal agents. PI(4,5)P2-septin regulation is crucial in early caspofungin responses and PKC-Mkc1 activation.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
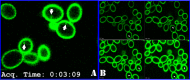
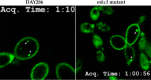
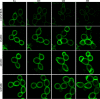

Similar articles
-
Rapid redistribution of phosphatidylinositol-(4,5)-bisphosphate and septins during the Candida albicans response to caspofungin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Sep;56(9):4614-24. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00112-12. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22687514 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of phosphatidylinositol-(4,5)-bisphosphate and active-Rho1p levels and distribution is crucial for correct spatio-temporal cytokinesis and echinocandin responses in Candida albicans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Jun 4;69(6):e0190024. doi: 10.1128/aac.01900-24. Epub 2025 May 5. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40323423 Free PMC article.
-
Efg1 Controls caspofungin-induced cell aggregation of Candida albicans through the adhesin Als1.Eukaryot Cell. 2011 Dec;10(12):1694-704. doi: 10.1128/EC.05187-11. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Eukaryot Cell. 2011. PMID: 22037180 Free PMC article.
-
Candida and candidaemia. Susceptibility and epidemiology.Dan Med J. 2013 Nov;60(11):B4698. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 24192246 Review.
-
Caspofungin resistance in Candida albicans: genetic factors and synergistic compounds for combination therapies.Braz J Microbiol. 2022 Sep;53(3):1101-1113. doi: 10.1007/s42770-022-00739-9. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Braz J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35352319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclic lipopeptides as membrane fusion inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2: New tricks for old dogs.Antiviral Res. 2023 Apr;212:105575. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2023.105575. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Antiviral Res. 2023. PMID: 36868316 Free PMC article.
-
Role of cell membrane homeostasis in the pathogenicity of pathogenic filamentous fungi.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2299183. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2023.2299183. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38156783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the caspofungin-induced cell wall damage response in Candida albicans.Curr Genet. 2020 Dec;66(6):1059-1068. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01105-8. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32876716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sur7 mediates a novel pathway for PI4,5P2 regulation in C. albicans that promotes stress resistance and cell wall morphogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Jul 1;35(7):ar99. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-08-0324. Epub 2024 May 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38776129 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Screening of Candida albicans Inactivation Mutants Identifies New Genes Involved in Macrophage-Fungal Cell Interactions.Front Microbiol. 2022 Apr 5;13:833655. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.833655. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35450285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andes DR, Safdar N, Baddley JW, Playford G, Reboli AC, Rex JH, Sobel JD, Pappas PG, Kullberg BJ. 2012. Impact of treatment strategy on outcomes in patients with candidemia and other forms of invasive candidiasis: a patient-level quantitative review of randomized trials. Clin Infect Dis 54:1110–1122. doi:10.1093/cid/cis021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cornely OA, Bassetti M, Calandra T, Garbino J, Kullberg BJ, Lortholary O, Meersseman W, Akova M, Arendrup MC, Arikan-Akdagli S, Bille J, Castagnola E, Cuenca-Estrella M, Donnelly JP, Groll AH, Herbrecht R, Hope WW, Jensen HE, Lass-Florl C, Petrikkos G, Richardson MD, Roilides E, Verweij PE, Viscoli C, Ullmann AJ. 2012. ESCMID* guideline for the diagnosis and management of Candida diseases 2012: non-neutropenic adult patients. Clin Microbiol Infect 18(Suppl 7):S19–S37. doi:10.1111/1469-0691.12039. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

