Selection of Reference Genes for Gene Expression Normalization in Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn under Abiotic Stresses, Hormone Treatments and Different Tissues
- PMID: 27022972
- PMCID: PMC4811526
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152356
Selection of Reference Genes for Gene Expression Normalization in Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn under Abiotic Stresses, Hormone Treatments and Different Tissues
Abstract
Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn is one of the main traditional Chinese medicines producing coumarins and plenty of literatures are focused on the biosynthesis of coumarins. Quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) is a widely used method in studying the biosynthesis pathway and the selection of reference genes plays a crucial role in accurate normalization. To facilitate biosynthesis study of coumarins, twelve candidate reference genes were selected from the transcriptome database of P. praeruptorum according to previous studies. Then, BestKeeper, geNoFrm and NormFinder were used for selecting stably expressed reference genes in different tissues and under various stress treatments. The results indicated that, among the twelve candidate reference genes, the SAND family protein (SAND), actin 2 (ACT2), ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 9 (UBC9), protein phosphatase 2A gene (PP2A) and polypyrimidine tract-binding protein (PTBP1) were the most stable reference genes under different experimental treatments, while glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and tubulin beta-6 (TUB6) were the least stable genes. In addition, the suitability of SAND, TIP41-like protein (TIP41), UBC9, ACT2, TUB6 and their combination as reference genes were confirmed by normalizing the expression of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase (ACO) in different treatments. This work is the first survey of the stability of reference genes in P. praeruptorum and provides guidelines to obtain more accurate qRT-PCR results in P. praeruptorum and other plant species.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
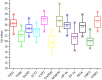
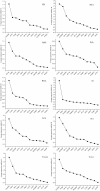


Similar articles
-
Selection and validation of appropriate reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR analysis in Momordica charantia.Phytochemistry. 2019 Aug;164:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.04.010. Epub 2019 May 2. Phytochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31054374
-
Selection of suitable reference genes for qPCR normalization under abiotic stresses in Oenanthe javanica (BI.) DC.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 20;9(3):e92262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092262. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24651080 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of reference genes for reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR normalization in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.).Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Dec 9;416(1-2):24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.10.105. Epub 2011 Nov 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 22086175
-
Identification and validation of reference genes for quantification of target gene expression with quantitative real-time PCR for tall fescue under four abiotic stresses.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 18;10(3):e0119569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119569. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25786207 Free PMC article.
-
Reference genes in real-time PCR.J Appl Genet. 2013 Nov;54(4):391-406. doi: 10.1007/s13353-013-0173-x. J Appl Genet. 2013. PMID: 24078518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals heat stress-responsive genes and their signalling pathways in lilies (Lilium longiflorum vs. Lilium distichum).PLoS One. 2020 Oct 2;15(10):e0239605. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239605. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33006971 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptomics Unveil the Crucial Genes Involved in Coumarin Biosynthesis in Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 17;13:899819. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.899819. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35656010 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of reference genes for qPCR normalization in buffalobur (Solanum rostratum Dunal).Sci Rep. 2019 May 6;9(1):6948. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43438-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31061419 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and functional characterization of a p-coumaroyl CoA 2'-hydroxylase involved in the biosynthesis of coumarin skeleton from Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn.Plant Mol Biol. 2017 Sep;95(1-2):199-213. doi: 10.1007/s11103-017-0650-4. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Plant Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28822035
-
Selection of the Reference Gene for Expression Normalization in Papaver somniferum L. under Abiotic Stress and Hormone Treatment.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jan 23;11(2):124. doi: 10.3390/genes11020124. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31979407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu J, Fong W, Zhang J, Leung C, Kwong H, Yang M, et al. Reversal of multidrug resistance in cancer cells by pyranocoumarins isolated from Radix Peucedani. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003; 473: 9–17. - PubMed
-
- Yu P, Jin H, Zhang J, Wang G, Li J, Zhu Z, et al. Pyranocoumarins isolated from Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in murine macrophages through inhibition of NF-κB and STAT3 activation. Inflammation. 2012; 35: 967–977. 10.1007/s10753-011-9400-y - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hou Z, Luo J, Wang J, Kong L. Separation of minor coumarins from Peucedanum praeruptorum using HSCCC and preparative HPLC guided by HPLC/MS. Sep Purif Technol. 2010; 75: 132–137.
-
- Ling-Yi K, Yi L, Zhi-Da M, Xian L, Ting-Ru Z. Coumarins from Peucedanum praeruptorum. Phytochemistry. 1996; 41: 1423–1426.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

