Using a Hybrid Model to Forecast the Prevalence of Schistosomiasis in Humans
- PMID: 27023573
- PMCID: PMC4847017
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph13040355
Using a Hybrid Model to Forecast the Prevalence of Schistosomiasis in Humans
Abstract
Background: We previously proposed a hybrid model combining both the autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) and the nonlinear autoregressive neural network (NARNN) models in forecasting schistosomiasis. Our purpose in the current study was to forecast the annual prevalence of human schistosomiasis in Yangxin County, using our ARIMA-NARNN model, thereby further certifying the reliability of our hybrid model.
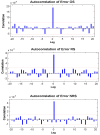
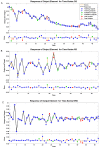
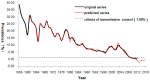
Methods: We used the ARIMA, NARNN and ARIMA-NARNN models to fit and forecast the annual prevalence of schistosomiasis. The modeling time range included was the annual prevalence from 1956 to 2008 while the testing time range included was from 2009 to 2012. The mean square error (MSE), mean absolute error (MAE) and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) were used to measure the model performance. We reconstructed the hybrid model to forecast the annual prevalence from 2013 to 2016.
Results: The modeling and testing errors generated by the ARIMA-NARNN model were lower than those obtained from either the single ARIMA or NARNN models. The predicted annual prevalence from 2013 to 2016 demonstrated an initial decreasing trend, followed by an increase.
Conclusions: The ARIMA-NARNN model can be well applied to analyze surveillance data for early warning systems for the control and elimination of schistosomiasis.
Keywords: ARIMA model; NARNN model; forecasting; hybrid model; schistosomiasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Time series model for forecasting the number of new admission inpatients.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2018 Jun 15;18(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12911-018-0616-8. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2018. PMID: 29907102 Free PMC article.
-
[Prediction of schistosomiasis infection rates of population based on ARIMA-NARNN model].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2016 Jul 12;28(6):630-634. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2016089. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 29469251 Chinese.
-
A hybrid model for predicting the prevalence of schistosomiasis in humans of Qianjiang City, China.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 13;9(8):e104875. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104875. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25119882 Free PMC article.
-
Autoregressive models in environmental forecasting time series: a theoretical and application review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Feb;30(8):19617-19641. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-25148-9. Epub 2023 Jan 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36648728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Application of Big Data Mining Technology in Monitoring and Early-warning of Schistosomiasis].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2015 Dec;33(6):461-5. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 27089777 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Spatiotemporal Frameworks for Infectious Disease Diffusion and Epidemiology.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016 Dec 20;13(12):1261. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13121261. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27999420 Free PMC article.
-
Forecasting the Tuberculosis Incidence Using a Novel Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition-Based Data-Driven Hybrid Model in Tibet, China.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 May 25;14:1941-1955. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S299704. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34079304 Free PMC article.
-
Time series model for forecasting the number of new admission inpatients.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2018 Jun 15;18(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12911-018-0616-8. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2018. PMID: 29907102 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of a deep learning approach for modeling seasonality and trends in hand-foot-mouth disease incidence in mainland China.Sci Rep. 2019 May 29;9(1):8046. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44469-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31142826 Free PMC article.
-
Time-Series Analysis for the Number of Foot and Mouth Disease Outbreak Episodes in Cattle Farms in Thailand Using Data from 2010-2020.Viruses. 2022 Jun 23;14(7):1367. doi: 10.3390/v14071367. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35891349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 10 Facts about Schistosomiasis. [(accessed on 2 December 2015)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/features/factfiles/schistosomiasis/en/
-
- Lei Z.L., Zheng H., Zhang L.J., Zhu R., Xu Z.M., Xu J., Fu Q., Wang Q., Li S.Z., Zhou X.N. Endemic status of schistosomiasis in People’s Republic of China in 2013. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control. 2014;26:591–597. (In Chinese) - PubMed
-
- Hao Y., Zheng H., Zhu R., Guo J.G., Wang L.Y., Chen Z., Zhou X.N. Schistosomiasis situation in People’s Republic of China in 2009. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control. 2010;22:521–527. (In Chinese)
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

