Robustness quantification methods comparison in volumetric modulated arc therapy to treat head and neck cancer
- PMID: 27025166
- PMCID: PMC4983261
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prro.2016.02.002
Robustness quantification methods comparison in volumetric modulated arc therapy to treat head and neck cancer
Abstract
Background: To compare plan robustness of volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) with intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and to compare the effectiveness of 3 plan robustness quantification methods.
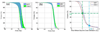
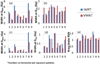
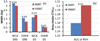
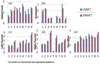
Methods and materials: The VMAT and IMRT plans were created for 9 head and neck cancer patients. For each plan, 6 new perturbed dose distributions were computed using ±3 mm setup deviations along each of the 3 orientations. Worst-case analysis (WCA), dose-volume histogram (DVH) band (DVHB), and root-mean-square dose-volume histogram (RVH) were used to quantify plan robustness. In WCA, a shaded area in the DVH plot bounded by the DVHs from the lowest and highest dose per voxel was displayed. In DVHB, we displayed the envelope of all DVHs in band graphs of all the 7 dose distributions. The RVH represents the relative volume on the vertical axis and the root-mean-square-dose on the horizontal axis. The width from the first 2 methods at different target DVH indices (such as D95% and D5%) and the area under the RVH curve for the target were used to indicate plan robustness. Results were compared using Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Results: The DVHB showed that the width at D95% of IMRT was larger than that of VMAT (unit Gy) (1.59 vs 1.18) and the width at D5% of IMRT was comparable to that of VMAT (0.59 vs 0.54). The WCA showed similar results between IMRT and VMAT plans (D95%: 3.28 vs 3.00; D5%: 1.68 vs 1.95). The RVH showed the area under the RVH curve of IMRT was comparable to that of VMAT (1.13 vs 1.15). No statistical significance was found in plan robustness between IMRT and VMAT.
Conclusions: The VMAT is comparable to IMRT in terms of plan robustness. For the 3 quantification methods, WCA and DVHB are DVH parameter-dependent, whereas RVH captures the overall effect of uncertainties.
Copyright © 2016 American Society for Radiation Oncology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Notification None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dosimetric comparison of distal esophageal carcinoma plans for patients treated with small-spot intensity-modulated proton versus volumetric-modulated arc therapies.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019 Jul;20(7):15-27. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12623. Epub 2019 May 21. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 31112371 Free PMC article.
-
Relative plan robustness of step-and-shoot vs rotational intensity-modulated radiotherapy on repeat computed tomographic simulation for weight loss in head and neck cancer.Med Dosim. 2016 Summer;41(2):154-8. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Med Dosim. 2016. PMID: 26993081
-
Multicriteria optimization informed VMAT planning.Med Dosim. 2014 Spring;39(1):64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Med Dosim. 2014. PMID: 24360919 Free PMC article.
-
Using overlap volume histogram and IMRT plan data to guide and automate VMAT planning: a head-and-neck case study.Med Phys. 2013 Feb;40(2):021714. doi: 10.1118/1.4788671. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23387737
-
Volumetric-modulated arc therapy vs. c-IMRT in esophageal cancer: a treatment planning comparison.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Oct 7;18(37):5266-75. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i37.5266. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23066322 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Robust optimization in IMPT using quadratic objective functions to account for the minimum MU constraint.Med Phys. 2018 Jan;45(1):460-469. doi: 10.1002/mp.12677. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29148570 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Plan Robustness Using Hybrid Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT) and Volumetric Arc Modulation Radiotherapy (VMAT) for Left-Sided Breast Cancer.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Mar 24;9(4):131. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9040131. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35447691 Free PMC article.
-
Small-spot intensity-modulated proton therapy and volumetric-modulated arc therapies for patients with locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A dosimetric comparative study.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2018 Nov;19(6):140-148. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12459. Epub 2018 Oct 17. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 30328674 Free PMC article.
-
Consideration of image guidance in patterns of failure analyses of intensity-modulated radiotherapy for head and neck cancer: a systematic review.Radiat Oncol. 2024 Mar 5;19(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13014-024-02421-w. Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38444011 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric comparison of distal esophageal carcinoma plans for patients treated with small-spot intensity-modulated proton versus volumetric-modulated arc therapies.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019 Jul;20(7):15-27. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12623. Epub 2019 May 21. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 31112371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vanetti E, Clivio A, Nicolini G, et al. Volumetric Arc modulated Radiotherapy for carcinomas of the Oropharynx, Hypopharynx and Larynx. A Treatment Planning Dosimetric Comparison with Fixed Field IMRT. Clinical Oncology. 2009;21:246–246. - PubMed
-
- Verbakel WFAR, Cuijpers JP, Hoffmans D, et al. VOLUMETRIC INTENSITYMODULATED ARC THERAPY VS. CONVENTIONAL IMRT IN HEAD-AND-NECK CANCER: A COMPARATIVE PLANNING AND DOSIMETRIC STUDY. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 2009;74:252–259. - PubMed
-
- Rao M, Yang W, Chen F, et al. Comparison of Elekta VMAT with helical tomotherapy and fixed field IMRT: Plan quality, delivery efficiency and accuracy. Medical Physics. 2010;37:1350–1359. - PubMed
-
- Bertelsen A, Hansen CR, Johansen J, et al. Single Arc Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy of head and neck cancer. Radiotherapy and Oncology. 2010;95:142–148. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Millan Barrachina J, Jerez Sainz I, Perez Rozos A, et al. Potential advantages of volumetric arc therapy in head and neck cancer. Head & neck. 2015;37:909–914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

