Going beyond the Control of Quorum-Sensing to Combat Biofilm Infections
- PMID: 27025518
- PMCID: PMC4810405
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics5010003
Going beyond the Control of Quorum-Sensing to Combat Biofilm Infections
Abstract
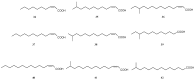
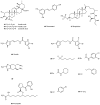
Most bacteria attach to surfaces where they form a biofilm, cells embedded in a complex matrix of polymers. Cells in biofilms are much better protected against noxious agents than free-living cells. As a consequence it is very difficult to control pathogens with antibiotics in biofilm infections and novel targets are urgently needed. One approach aims at the communication between cells to form and to maintain a biofilm, a process called quorum-sensing. Water soluble small-sized molecules mediate this process and a number of antagonists of these compounds have been found. In this review natural compounds and synthetic drugs which do not interfere with the classical quorum-sensing compounds are discussed. For some of these compounds the targets are still not known, but others interfere with the formation of exopolysaccharides, virulence factors, or cell wall synthesis or they start an internal program of biofilm dispersal. Some of their targets are more conserved among pathogens than the receptors for quorum sensing autoinducers mediating quorum-sensing, enabling a broader application of the drug. The broad spectrum of mechanisms, the diversity of bioactive compounds, their activity against several targets, and the conservation of some targets among bacterial pathogens are promising aspects for several clinical applications of this type of biofilm-controlling compound in the future.
Keywords: biofilm dispersal; biofilm infection; quorum sensing.
Figures
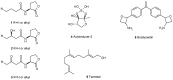
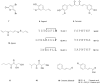
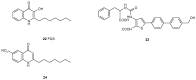
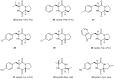
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

