A Clinical Drug Library Screen Identifies Tosufloxacin as Being Highly Active against Staphylococcus aureus Persisters
- PMID: 27025627
- PMCID: PMC4790289
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics4030329
A Clinical Drug Library Screen Identifies Tosufloxacin as Being Highly Active against Staphylococcus aureus Persisters
Abstract
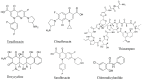
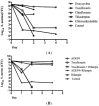
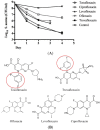
To identify effective compounds that are active against Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) persisters, we screened a clinical drug library consisting of 1524 compounds and identified six drug candidates that had anti-persister activity: tosufloxacin, clinafloxacin, sarafloxacin, doxycycline, thiostrepton, and chlorosalicylanilide. Among them, tosufloxacin had the highest anti-persister activity, which could completely eradicate S. aureus persisters within 2 days in vitro. Clinafloxacin ranked the second with very few persisters surviving the drug exposure. Interestingly, we found that both tosufloxacin and trovafloxacin that had high activity against persisters contained at the N-1 position the 2,4-difluorophenyl group, which is absent in other less active quinolones and may be associated with the high anti-persister activity. Further studies are needed to evaluate tosufloxacin in animal models and to explain its unique activity against bacterial persisters. Our findings may have implications for improved treatment of persistent bacterial infections.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; clinafloxacin; clinical drug library; persisters; tosufloxacin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Anti-Persister Activity against Uropathogenic Escherichia coli from a Clinical Drug Library.Antibiotics (Basel). 2015 May 12;4(2):179-87. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics4020179. Antibiotics (Basel). 2015. PMID: 27025620 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Genes Involved in Escherichia coli Persistence to Tosufloxacin.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Sep 30;10:581986. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.581986. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33117736 Free PMC article.
-
Eradication of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Infection by Persister Drug Combination.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Sep 20;11(10):1278. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101278. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36289936 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus chronic and relapsing infections: Evidence of a role for persister cells: An investigation of persister cells, their formation and their role in S. aureus disease.Bioessays. 2014 Oct;36(10):991-6. doi: 10.1002/bies.201400080. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Bioessays. 2014. PMID: 25100240 Review.
-
Multidrug tolerance of biofilms and persister cells.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;322:107-31. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75418-3_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18453274 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial persisters: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic development.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Jul 17;9(1):174. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01866-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39013893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound-Mediated Antibiotic Delivery to In Vivo Biofilm Infections: A Review.Chembiochem. 2024 Oct 16;25(20):e202400181. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202400181. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Chembiochem. 2024. PMID: 38924307 Review.
-
Synergistic effect of antibiotic combinations on Staphylococcus aureus biofilms and their persister cell populations.Biofilm. 2022 Feb 2;4:100068. doi: 10.1016/j.bioflm.2022.100068. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biofilm. 2022. PMID: 35198967 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Neurodegenerative Diseases on Drug Binding to Brain Tissues: From Animal Models to Human Samples.Neurotherapeutics. 2018 Jul;15(3):742-750. doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-0624-5. Neurotherapeutics. 2018. PMID: 29675823 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of antibiotics that selectively kill metabolically dormant bacteria.Cell Chem Biol. 2024 Apr 18;31(4):712-728.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.10.026. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Cell Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38029756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bigger J. Treatment of staphylococcal infections with penicillin by intermittent sterilization. Lancet. 1944;244:497–500. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)74210-3. - DOI
-
- Bernthal N.M., Stavrakis A.I., Billi F., Cho J.S., Kremen T.J., Simon S.I., Cheung A.L., Finerman G.A., Lieberman J.R., Adams J.S., et al. A mouse model of post-arthroplasty Staphylococcus aureus joint infection to evaluate in vivo the efficacy of antimicrobial implant coatings. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e12580. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012580. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

