Short, Synthetic Cationic Peptides Have Antibacterial Activity against Mycobacterium smegmatis by Forming Pores in Membrane and Synergizing with Antibiotics
- PMID: 27025629
- PMCID: PMC4790291
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics4030358
Short, Synthetic Cationic Peptides Have Antibacterial Activity against Mycobacterium smegmatis by Forming Pores in Membrane and Synergizing with Antibiotics
Abstract
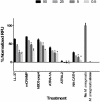
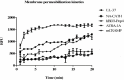
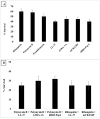
Multicellular organisms are constantly exposed to a multitude of pathogenic microbes. Infection is inhibited in vivo by the innate and adaptive immune system. Mycobacterium species have emerged that are resistant to most antibiotics. We identified several naturally occurring cationic antimicrobial peptides that were active at low micromolar concentrations against Mycobacterium smegmatis. Human-derived cathelicidin LL-37 is well characterized and studied against M. smegmatis; we compared LL-37 with Chinese cobra-derived cathelicidin NA-CATH and mouse cathelicidin (mCRAMP). Two synthetic 11-residue peptides (ATRA-1A and ATRA-2) containing variations of a repeated motif within NA-CATH were tested for their activity against M. smegmatis along with a short synthetic peptide derivative from the human beta-defensin hBD3 (hBD3-Pep4). We hypothesized that these smaller synthetic peptides may demonstrate antimicrobial effectiveness with shorter length (and at less cost), making them strong potential candidates for development into broad-spectrum antimicrobial compounds or use in combination with antibiotics. These peptides have antimicrobial activity with EC50 ranging from 0.05 to 1.88 μg/mL against Mycobacterium smegmatis. The ATRA-1A short peptide was found to be the most effective antimicrobial peptide (AMP) (EC50 = 0.05 μg/mL). High bactericidal activity correlated with bacterial membrane depolarization and permeabilization activities. The efficacy of the peptides was further analyzed through Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) assays. The MICs were determined by the microdilution method. The peptide mCRAMP showed the best MIC activity at 15.6 μg/mL. Neither of the effective short synthetic peptides demonstrated synergy with the antibiotic rifampicin, although both demonstrated synergy with the cyclic peptide antibiotic polymyxin B. The peptides LL-37 and mCRAMP displayed synergism with rifampicin in MIC assays, whereas antibiotic polymyxin B displayed synergism with LL-37, ATRA-1A, and hBD3-Pep4. In further studies, polymyxin B synergized with LL-37, ATRA-1A, and hBD3-Pep4 while Rifampicin synergized with LL-37 and mCRAMP for intracellular killing of mycobacteria residing inside macrophages. These studies provide the foundation for the potential development of synthetic cationic antimicrobial peptides with activity against mycobacteria.
Keywords: antibiotics; cationic AMPs; mycobacterium; synergy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of cathelicidins and short, synthetic peptides against Francisella.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 May 28;396(2):246-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.073. Epub 2010 Apr 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20399752
-
Snake Cathelicidin NA-CATH and Smaller Helical Antimicrobial Peptides Are Effective against Burkholderia thailandensis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 Jul 21;9(7):e0003862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003862. eCollection 2015. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 26196513 Free PMC article.
-
Natural and synthetic cathelicidin peptides with anti-microbial and anti-biofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus.BMC Microbiol. 2011 May 23;11:114. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-114. BMC Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21605457 Free PMC article.
-
The Human Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37 and Mimics are Potential Anticancer Drugs.Front Oncol. 2015 Jun 30;5:144. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00144. eCollection 2015. Front Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26175965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Recent Research into the Effects of Antimicrobial Peptides on Biofilms-January 2020 to September 2023.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Apr 9;13(4):343. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13040343. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Determinants of Antibiotic Resistance in Francisella.Front Microbiol. 2021 May 12;12:644855. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.644855. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34054749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hitchhiking with Nature: Snake Venom Peptides to Fight Cancer and Superbugs.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Apr 15;12(4):255. doi: 10.3390/toxins12040255. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32326531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The antimicrobial peptide Esc(1-21)-1c increases susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to conventional antibiotics by decreasing the expression of the MexAB-OprM efflux pump.Front Chem. 2023 Oct 24;11:1271153. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1271153. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37942400 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Functional Characterization of Peptides With Antimicrobial Activity From the Syphilis Spirochete, Treponema pallidum.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 3;13:888525. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.888525. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35722306 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting chitosan and gold nanoparticles for antimycobacterial activity of in silico identified antimicrobial motif of human neutrophil peptide-1.Sci Rep. 2019 May 27;9(1):7866. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44256-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31133658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prasad R. Multidrug and extensively drug-resistant TB (M/XDR-TB): Problems and solutions. Indian J. Tuberc. 2010;57:180–191. - PubMed
-
- Niyonsaba F., Ushio H., Hara M., Yokoi H., Tominaga M., Takamori K., Kajiwara N., Saito H., Nagaoka I., Ogawa H., et al. Antimicrobial peptides human beta-defensins and cathelicidin LL-37 induce the secretion of a pruritogenic cytokine IL-31 by human mast cells. J. Immunol. 2010;184:3526–3534. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900712. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

