Measures of Urinary Protein and Albumin in the Prediction of Progression of IgA Nephropathy
- PMID: 27026518
- PMCID: PMC4891752
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.10150915
Measures of Urinary Protein and Albumin in the Prediction of Progression of IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
Background and objectives: Proteinuria is an independent predictor for IgA nephropathy (IgAN) progression. Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR), protein-to-creatinine ratio, and 24-hour urine protein excretion (UPE) are widely used for proteinuria evaluation in clinical practice. Here, we evaluated the association of these measurements with clinical and histologic findings of IgAN and explored which was the best predictor of IgAN prognosis.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Patients with IgAN were followed up for ≥12 months, were diagnosed between 2003 and 2012, and had urine samples available (438 patients). Spot urine ACR, protein-to-creatinine ratio, and 24-hour UPE at the time of renal biopsy were measured on a Hitachi Automatic Biochemical Analyzer 7180 (Hitachi, Yokohama, Japan).
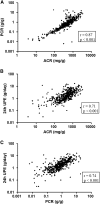
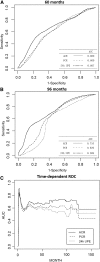
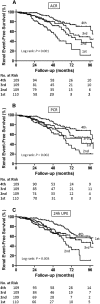
Results: In our patients, ACR, protein-to-creatinine ratio, and 24-hour UPE were highly correlated (correlation coefficients: 0.71-0.87). They showed good relationships with acknowledged markers reflecting IgAN severity, including eGFR, hypertension, and the biopsy parameter (Oxford severity of tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis parameter). However, only ACR presented with positive association with the Oxford segmental glomerulosclerosis/adhesion parameter and extracapillary proliferation lesions. The follow-up time was 37.0 (22.0-58.0) months, with the last follow-up on April 18, 2014. In total, 124 patients reached the composite end point (30% eGFR decline, ESRD, or death). In univariate survival analysis, ACR consistently had better performance than protein-to-creatinine ratio and 24-hour UPE as represented by higher area under the curve using time-dependent survival analysis. When adjusted for well known risk factors for IgAN progression, ACR was most significantly associated with the composite end point (hazard ratio, 1.56 per 1-SD change of standard normalized square root-transformed ACR; 95% confidence interval, 1.29 to 1.89; P<0.001). Compared with protein-to-creatinine ratio and 24-hour UPE, addition of ACR to traditional risk factors resulted in more improvement in the predictive ability of IgAN progression (c statistic: ACR=0.70; protein-to-creatinine ratio =0.68; 24-hour UPE =0.69; Akaike information criterion: ACR=1217.85; protein-to-creatinine ratio =1229.28; 24-hour UPE =1234.96; P<0.001).
Conclusions: In IgAN, ACR, protein-to-creatinine ratio, and 24-hour UPE had comparable association with severe clinical and histologic findings. Compared with protein-to-creatinine ratio and 24-hour UPE, ACR showed slightly better performance in predicting IgAN progression.
Keywords: Follow-Up Studies; Glomerulonephritis, IGA; Humans; IgA nephropathy; Kidney Failure, Chronic; Prognosis; Urinalysis; albuminuria; creatinine; proteinuria.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio is a reliable indicator for evaluating complications of chronic kidney disease and progression in IgA nephropathy in China.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2016 May;71(5):243-50. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2016(05)01. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2016. PMID: 27276392 Free PMC article.
-
A predictive clinical grading system for immunoglobulin A nephropathy by combining proteinuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate.Nephron Clin Pract. 2011;118(3):c292-300. doi: 10.1159/000322613. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011. PMID: 21212693
-
Predictive value of spot versus 24-hour measures of proteinuria for death, end-stage kidney disease or chronic kidney disease progression.BMC Nephrol. 2018 Mar 7;19(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-0853-1. BMC Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29514605 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Treatment Effects on Early Change in Urine Protein and Treatment Effects on GFR Slope in IgA Nephropathy: An Individual Participant Meta-analysis.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Sep;78(3):340-349.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.03.007. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 33775708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic review of the application of the Kidney Failure Risk Equation and Oxford classification in estimating prognosis in IgA Nephropathy.Syst Rev. 2025 Jan 16;14(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02739-2. Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39819700 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Intensive Systolic Blood Pressure Lowering and Kidney Disease Progression in IgA Nephropathy: A Cohort Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 16;9:813603. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.813603. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35252253 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease.Drugs. 2019 Mar;79(4):365-379. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1064-1. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30758803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary GADD45G Protein Excretion Is Associated with IgA Nephropathy Progression.Biomedicines. 2024 Dec 14;12(12):2846. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122846. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767752 Free PMC article.
-
An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts IgA nephropathy severity and progression.MedComm (2020). 2024 Nov 3;5(11):e783. doi: 10.1002/mco2.783. eCollection 2024 Nov. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39492831 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of 24-h Urine Protein Excretion Using Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio from an In-Hospital Population.Med Sci Monit. 2022 Feb 11;28:e934307. doi: 10.12659/MSM.934307. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 35145052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D’Amico G: The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q J Med 64: 709–727, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Donadio JV, Grande JP: IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med 347: 738–748, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Coppo R, Amore A: Aberrant glycosylation in IgA nephropathy (IgAN). Kidney Int 65: 1544–1547, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Novak J, Tomana M, Kilian M, Coward L, Kulhavy R, Barnes S, Mestecky J: Heterogeneity of O-glycosylation in the hinge region of human IgA1. Mol Immunol 37: 1047–1056, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Schena FP: A retrospective analysis of the natural history of primary IgA nephropathy worldwide. Am J Med 89: 209–215, 1990 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

