Adiponectin levels predict prediabetes risk: the Pathobiology of Prediabetes in A Biracial Cohort (POP-ABC) study
- PMID: 27026810
- PMCID: PMC4800069
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2016-000194
Adiponectin levels predict prediabetes risk: the Pathobiology of Prediabetes in A Biracial Cohort (POP-ABC) study
Abstract
Background: Adiponectin levels display ethnic disparities, and are inversely associated with the risk of type 2 diabetes (T2DM). However, the association of adiponectin with prediabetes risk in diverse populations has not been well-studied. Here, we assessed baseline adiponectin levels in relation to incident prediabetes in a longitudinal biracial cohort.
Research design and methods: The Pathobiology of Prediabetes in A Biracial Cohort study followed non-diabetic offspring of parents with T2DM for the occurrence of prediabetes, defined as impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance. Assessments at enrollment and during follow-up included a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test, anthropometry, biochemistries (including fasting insulin and adiponectin levels), insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion. Logistic regression was used to evaluate the contribution of adiponectin to risk of progression to prediabetes.
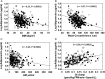
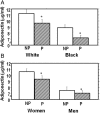
Results: Among the 333 study participants (mean (SD) age 44.2 (10.6) year), 151(45.3%) were white and 182 (54.8%) were black. During approximately 5.5 (mean 2.62) years of follow-up, 110 participants (33%) progressed to prediabetes (N=100) or T2DM (N=10), and 223 participants (67%) were non-progressors. The mean cohort adiponectin level was 9.41+5.30 μg/mL (range 3.1-45.8 μg/mL); values were higher in women than men (10.3+5.67 μg/mL vs 7.27+3.41 μg/mL, p<0.0001) and in white than black offspring (10.7+5.44 μg/mL vs 8.34+4.95 μg/mL, p<0.0001). Adiponectin levels correlated inversely with adiposity and glycemia, and positively with insulin sensitivity and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Baseline adiponectin strongly predicted incident prediabetes: the HR for prediabetes per 1 SD (approximately 5 μg/mL) higher baseline adiponectin was 0.48 (95% CI 0.27 to 0.86, p=0.013).
Conclusions: Among healthy white and black adults with parental history of T2DM, adiponectin level is a powerful risk marker of incident prediabetes. Thus, the well-known association of adiponectin with diabetes risk is evident at a much earlier stage in pathogenesis, during transition from normoglycemia to prediabetes.
Keywords: Adiponectin; Impaired Fasting Glucose; Impaired Glucose Tolerance; Insulin Sensitivity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lack of racial disparity in incident prediabetes and glycemic progression among black and white offspring of parents with type 2 diabetes: the pathobiology of prediabetes in a biracial cohort (POP-ABC) study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Jun;99(6):E1078-87. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-1077. Epub 2014 Mar 14. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24628558 Free PMC article.
-
Association of bone mineral density with prediabetes risk among African-American and European-American adult offspring of parents with type 2 diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 5;13:1065527. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1065527. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36686435 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma lipid levels predict dysglycemia in a biracial cohort of nondiabetic subjects: Potential mechanisms.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016 Nov;241(17):1961-1967. doi: 10.1177/1535370216659946. Epub 2016 Jul 17. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016. PMID: 27430991 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary habits and leisure-time physical activity in relation to adiposity, dyslipidemia, and incident dysglycemia in the pathobiology of prediabetes in a biracial cohort study.Metabolism. 2015 Sep;64(9):1060-7. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.05.015. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Metabolism. 2015. PMID: 26116207 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of adiponectin in prediabetes: strategies, challenges, and future directions.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Jan 18;15:20420188231222371. doi: 10.1177/20420188231222371. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38250316 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glycemic and metabolic sub-classification of prediabetes and risk factors for cardiovascular disease in the D2d cohort.Am J Prev Cardiol. 2023 Jul 27;15:100525. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpc.2023.100525. eCollection 2023 Sep. Am J Prev Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37650052 Free PMC article.
-
Adipokines Regulate the Expression of Tumor-Relevant MicroRNAs.Obes Facts. 2019;12(2):211-225. doi: 10.1159/000496625. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Obes Facts. 2019. PMID: 30999294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcome of lifestyle intervention in relation to duration of pre-diabetes: the Pathobiology and Reversibility of Prediabetes in a Biracial Cohort (PROP-ABC) study.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2022 Mar;10(2):e002748. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002748. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2022. PMID: 35273012 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Insulin and Proinsulin Dynamics Progressively Deteriorate From Within the Normal Range Toward Impaired Glucose Tolerance.J Endocr Soc. 2020 Jun 5;4(7):bvaa066. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaa066. eCollection 2020 Jul 1. J Endocr Soc. 2020. PMID: 32617449 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Specific Modulation of Fetal Adipogenesis by Gestational Bisphenol A and Bisphenol S Exposure.Endocrinology. 2017 Nov 1;158(11):3844-3858. doi: 10.1210/en.2017-00615. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28938450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Snehalatha C, Mukesh B, Simon M et al. . Plasma adiponectin is an independent predictor of type 2 diabetes in Asian Indians. Diabetes Care 2003;26:3226–9. - PubMed
-
- Halperin F, Beckman JA, Patti ME et al. . The role of total and high molecular-weight complex of adiponectin in vascular function in offspring whose parents both had type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2005;48:2147–54. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
