Genetic control of cell division patterns in the Drosophila embryo
- PMID: 2702688
- PMCID: PMC2755076
- DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90183-9
Genetic control of cell division patterns in the Drosophila embryo
Abstract
In Drosophila embryogenesis, mitotic control undergoes a significant transition during the 14th interphase. Mitoses before interphase 14 run on maternal products, and occur in metasynchronous waves. Mitoses after interphase 14 require zygotic transcription, and occur asyncronously in an intricate, highly ordered spatio-temporal pattern. Mutations at the string (stg) locus cause cell-cycle arrest during this transition, in G2 of interphase 14, yet do not arrest other aspects of development. This phenotype suggests that stg is required specifically for initiating mitosis. We describe the cloning of stg, and show that its predicted amino acid sequence is homologous to that of cdc25, a regular of mitotic initiation in the yeast S. pombe. In addition, we show that zygotic expression of stg mRNA occurs in a dynamic series of spatial patterns which anticipate the patterns of the zygotically driven cell divisions. Therefore we suggest that regulated expression of stg mRNA controls the timing and location of these embryonic cell divisions.
Figures
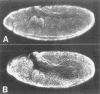
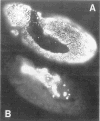





References
-
- Arion D, Meijer L, Brizuela L, Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase–specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988;55:371–378. - PubMed
-
- Blow JJ, Laskey RA. A role for the nuclear envelope in controlling DNA replication within the cell cycle. Nature. 1988;332:546–548. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal AB, Kriegstein HJ, Hogness DS. The units of DNA replication in Drosophila melanogaster chromosomes. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:205–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

