BISPHOSPHONATE-INDUCED MAXILLOFACIAL OSTEONECROSIS IN OSTEOPOROTIC INDIVIDUALS
- PMID: 27027044
- PMCID: PMC4799289
- DOI: 10.1016/S2255-4971(15)30402-X
BISPHOSPHONATE-INDUCED MAXILLOFACIAL OSTEONECROSIS IN OSTEOPOROTIC INDIVIDUALS
Abstract
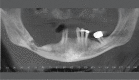
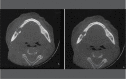
Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the maxillae may be an important complication of long-term osteoporosis treatment. The possibility of osteonecrosis of the maxillae in patients exposed to nitrogenated bisphosphonates was first described in 2003. Since then, case reports and retrospective studies have demonstrated higher percentages of occurrence of osteonecrosis in patients who have used or are using bisphosphonates. Although this complication may be spontaneous, invasive oral procedures have a role as risk factors associated with dental procedures such as tooth extractions and other bone operations. In addition, tooth infections and periodontal disease have been reported to be the main risk factors for development of bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis of the maxillae. For this reason, dentists, general clinicians, orthopedists, geriatricians and oral-maxillofacial surgeons need to be aware of this problem and work in a multidisciplinary environment, thereby stimulating early diagnosis and prevention of further potential cases.
Keywords: Bisphosphonates; Facial Bones; Osteoporosis.
Figures
References
-
- NIH Consensus Development Panel on Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy, March 7-29, 2000: highlights of the conference. South Med J. 2001;94(6):569–573. - PubMed
-
- Harvey N, Dennison E, Cooper C. Osteoporosis: impact on health and economics. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010 Feb;6(2):99–105. - PubMed
-
- Rao SS, Budhwar N, Ashfaque A. Osteoporosis in men. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82(5):503–508. - PubMed
-
- Fernández-Tresguerres-Hernández-Gil I, Alobera-Gracia MA, del-Canto-Pingarrón M, Blanco-Jerez L. Physiological bases of bone regeneration I. Histology and physiology of bone tissue. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2006;11(1):E47–E51. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources