Candidalysin is a fungal peptide toxin critical for mucosal infection
- PMID: 27027296
- PMCID: PMC4851236
- DOI: 10.1038/nature17625
Candidalysin is a fungal peptide toxin critical for mucosal infection
Abstract
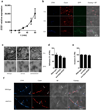
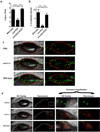
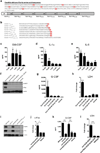
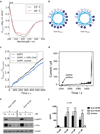
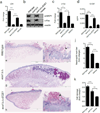
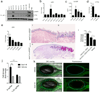
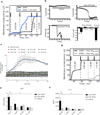
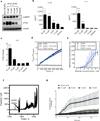
Cytolytic proteins and peptide toxins are classical virulence factors of several bacterial pathogens which disrupt epithelial barrier function, damage cells and activate or modulate host immune responses. Such toxins have not been identified previously in human pathogenic fungi. Here we identify the first, to our knowledge, fungal cytolytic peptide toxin in the opportunistic pathogen Candida albicans. This secreted toxin directly damages epithelial membranes, triggers a danger response signalling pathway and activates epithelial immunity. Membrane permeabilization is enhanced by a positive charge at the carboxy terminus of the peptide, which triggers an inward current concomitant with calcium influx. C. albicans strains lacking this toxin do not activate or damage epithelial cells and are avirulent in animal models of mucosal infection. We propose the name 'Candidalysin' for this cytolytic peptide toxin; a newly identified, critical molecular determinant of epithelial damage and host recognition of the clinically important fungus, C. albicans.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Information Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints. The authors declare no competing financial interests. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to BHu (bernhard.hube@leibniz-hki.de).
Figures


Comment in
-
Microbiology: Fungus produces a toxic surprise.Nature. 2016 Apr 7;532(7597):41-2. doi: 10.1038/nature17319. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27027285 No abstract available.
-
Fungal Pathogenesis: Candida's toxic relationship with its host.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Apr;14(5):268. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.53. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27067400 No abstract available.
References
Extended Data Table references
-
- Gillum AM, Tsay EY, Kirsch DR. Isolation of the Candida albicans gene for orotidine-5′-phosphate decarboxylase by complementation of S. cerevisiae ura3, E. coli pyrF mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198:179–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

