Genome-wide Association Study of Cannabis Dependence Severity, Novel Risk Variants, and Shared Genetic Risks
- PMID: 27028160
- PMCID: PMC4974817
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0036
Genome-wide Association Study of Cannabis Dependence Severity, Novel Risk Variants, and Shared Genetic Risks
Abstract
Importance: Cannabis dependence (CAD) is a serious problem worldwide and is of growing importance in the United States because cannabis is increasingly available legally. Although genetic factors contribute substantially to CAD risk, at present no well-established specific genetic risk factors for CAD have been elucidated.
Objective: To report findings for DSM-IV CAD criteria from association analyses performed in large cohorts of African American and European American participants from 3 studies of substance use disorder genetics.
Design, setting, and participants: This genome-wide association study for DSM-IV CAD criterion count was performed in 3 independent substance dependence cohorts (the Yale-Penn Study, Study of Addiction: Genetics and Environment [SAGE], and International Consortium on the Genetics of Heroin Dependence [ICGHD]). A referral sample and volunteers recruited in the community and from substance abuse treatment centers included 6000 African American and 8754 European American participants, including some from small families. Participants from the Yale-Penn Study were recruited from 2000 to 2013. Data were collected for the SAGE trial from 1990 to 2007 and for the ICGHD from 2004 to 2009. Data were analyzed from January 2, 2013, to November 9, 2015.
Main outcomes and measures: Criterion count for DSM-IV CAD.
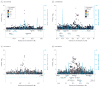
Results: Among the 14 754 participants, 7879 were male, 6875 were female, and the mean (SD) age was 39.2 (10.2) years. Three independent regions with genome-wide significant single-nucleotide polymorphism associations were identified, considering the largest possible sample. These included rs143244591 (β = 0.54, P = 4.32 × 10-10 for the meta-analysis) in novel antisense transcript RP11-206M11.7;rs146091982 (β = 0.54, P = 1.33 × 10-9 for the meta-analysis) in the solute carrier family 35 member G1 gene (SLC35G1); and rs77378271 (β = 0.29, P = 2.13 × 10-8 for the meta-analysis) in the CUB and Sushi multiple domains 1 gene (CSMD1). Also noted was evidence of genome-level pleiotropy between CAD and major depressive disorder and for an association with single-nucleotide polymorphisms in genes associated with schizophrenia risk. Several of the genes identified have functions related to neuronal calcium homeostasis or central nervous system development.
Conclusions and relevance: These results are the first, to our knowledge, to identify specific CAD risk alleles and potential genetic factors contributing to the comorbidity of CAD with major depression and schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Genome-wide Significant Associations for Cannabis Dependence Severity: Relevance to Psychiatric Disorders.JAMA Psychiatry. 2016 May 1;73(5):443-4. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0046. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27027914 No abstract available.
References
-
- United Nation Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) [Accessed February 18, 2016];Cannabis: A Short Review. https://www.unodc.org/documents/drug-prevention-and-treatment/cannabis_r.... Published 2012.
-
- Volkow ND, Compton WM, Weiss SR. Adverse health effects of marijuana use. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(9):879. - PubMed
-
- Wölfling K, Flor H, Grüsser SM. Psychophysiological responses to drug-associated stimuli in chronic heavy cannabis use. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27(4):976–983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- RC2 DA028909/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HG065403/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018432/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004422/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA013423/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA011330/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA017535/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA089392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 AA008401/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016359/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

