Nicotine-Induced Apoptosis in Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 27028622
- PMCID: PMC4814027
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152591
Nicotine-Induced Apoptosis in Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells
Abstract
Background: Nicotine is, to a large extent, responsible for smoking-mediated renal dysfunction. This study investigated nicotine's effects on renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis in vitro and it explored the mechanisms underlying its effects.
Methods: Human proximal tubular epithelial (HK-2) cells were treated with nicotine. Cell viability was examined by using the WST-1 assay. Intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) proteins were determined. The messenger ribonucleic acid and the protein expression associated with the nicotine acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) in HK-2 cells was examined, and apoptosis was detected using flow cytometry, cell cycle analysis, and immunoblot analysis.
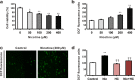
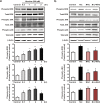
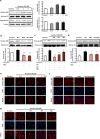
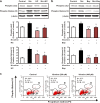
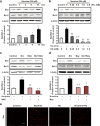
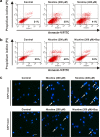
Results: The HK-2 cells were endowed with nAChRs. Nicotine treatment reduced cell viability dose dependently, increased ROS levels, and increased extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 MAPK expression. Nicotine increased NF-κB activation, which was attenuated by N-acetyl-L-cysteine, and ERK and JNK inhibitors, but was not affected by a p38 MAPK inhibitor. Nicotine increased the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, which was attenuated by N-acetyl-L-cysteine, the NF-κB inhibitor, Bay 11-7082, and hexamethonium, a non-specific nAChR blocker. Flow cytometry revealed nicotine-induced G2/M phase arrest. While nicotine treatment increased the expression of phosphorylated cdc2 and histone H3, a marker of G2/M phase arrest, hexamethonium and Bay 11-7082 pretreatment reduced their expression.
Conclusions: Nicotine caused apoptosis in HK-2 cells by inducing ROS generation that activated the NF-κB signaling pathway via the MAPK pathway and it arrested the cell cycle at the G2/M phase. Nicotine-induced apoptosis in HK-2 cells involves the nAChRs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal-induced apoptosis in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011 Dec;26(12):3866-73. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr386. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21771752
-
Aristolochic acid-induced apoptosis and G2 cell cycle arrest depends on ROS generation and MAP kinases activation.Arch Toxicol. 2015 Jan;89(1):47-56. doi: 10.1007/s00204-014-1249-z. Epub 2014 May 4. Arch Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 24792323
-
Macrophage-stimulating protein attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in human renal HK-2 cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 5;715(1-3):304-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.05.006. Epub 2013 May 29. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23726950
-
Molecular chemotherapeutic potential of butein: A concise review.Food Chem Toxicol. 2018 Feb;112:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.12.028. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29258953 Review.
-
Nicotine-induced resistance of non-small cell lung cancer to treatment--possible mechanisms.Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016 Mar 4;70:186-93. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1196391. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016. PMID: 26943316 Review.
Cited by
-
Duration-dependent effects of nicotine exposure on growth and AKT activation in human kidney epithelial cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2018 Nov;448(1-2):51-60. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3312-1. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29396723
-
Antioxidant Systems, lncRNAs, and Tunneling Nanotubes in Cell Death Rescue from Cigarette Smoke Exposure.Cells. 2022 Jul 23;11(15):2277. doi: 10.3390/cells11152277. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35892574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotine exacerbates tacrolimus-induced renal injury by programmed cell death.Korean J Intern Med. 2021 Nov;36(6):1437-1449. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2021.326. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Korean J Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 34666433 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of Nicotine-Induced Osteoarthritis by Platelet-Derived Biomaterials Through Modulating IGF-1/AKT/IRS-1 Signaling Axis.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720947348. doi: 10.1177/0963689720947348. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32757664 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Exposure to Cigarette Smoking Followed by Myocardial Infarction Aggravates Renal Damage in an In Vivo Mouse Model.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:5135241. doi: 10.1155/2017/5135241. Epub 2017 Oct 22. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 29177025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartecchi CE, MacKenzie TD, Schrier RW. The human costs of tobacco use (1). N Engl J Med. 1994;330:907–12. - PubMed
-
- Bleyer AJ, Shemanski LR, Burke GL, Hansen KJ, Appel RG. Tobacco, hypertension, and vascular disease: risk factors for renal functional decline in an older population. Kidney Int. 2000;57:2072–9. - PubMed
-
- Regalado M, Yang S, Wesson DE. Cigarette smoking is associated with augmented progression of renal insufficiency in severe essential hypertension. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;35:687–94. - PubMed
-
- Rossing P, Hougaard P, Parving HH. Risk factors for development of incipient and overt diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients: a 10-year prospective observational study. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:859–64. - PubMed
-
- Stegmayr BG. A study of patients with diabetes mellitus (type 1) and end-stage renal failure: tobacco usage may increase risk of nephropathy and death. J Intern Med. 1990;228:121–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

