Locomotor, discriminative stimulus, and place conditioning effects of MDAI in rodents
- PMID: 27028902
- PMCID: PMC4965292
- DOI: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000237
Locomotor, discriminative stimulus, and place conditioning effects of MDAI in rodents
Abstract
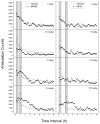
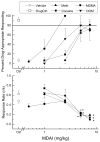
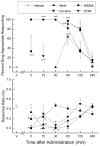
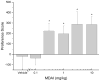
5,6-Methylenedioxy-2-aminoindane (MDAI) has become a common substitute for (±)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in Ecstasy. MDAI is known to produce MDMA-like discriminative stimulus effects, but it is not known whether MDAI has psychostimulant or hallucinogen-like effects. MDAI was tested for locomotor stimulant effects in mice and subsequently for discriminative stimulus effects in rats trained to discriminate cocaine (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneally), methamphetamine (1 mg/kg, intraperitoneally), ±MDMA (1.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally), or (-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine hydrochloride (0.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) from saline. The ability of MDAI to produce conditioned place preference was also tested in mice. MDAI (3 to 30 mg/kg) depressed locomotor activity from 10 to 60 min. A rebound stimulant effect was observed at 1 to 3.5 h following 30 mg/kg. Lethality occurred in 8/8 mice following 100 mg/kg MDAI. Similarly, MDMA depressed locomotor activity immediately following the administration of 0.25 mg/kg and stimulant effects were observed 50-70 min following the administration of 0.5 and 1 mg/kg. MDAI fully substituted for the discriminative stimulus effects of MDMA (2.5 mg/kg), (-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine hydrochloride (5 mg/kg), and cocaine (7.5 mg/kg), but produced only 73% methamphetamine-appropriate responding at a dose that suppressed responding (7.5 mg/kg). MDAI produced tremors at 10 mg/kg in one methamphetamine-trained rat. MDAI produced conditioned place preference from 0.3 to 10 mg/kg. The effects of MDAI on locomotor activity and drug discrimination were similar to those produced by MDMA, having both psychostimulant-like and hallucinogen-like effects; thus, MDAI may have similar abuse potential as MDMA.
Figures
References
-
- Bilsky EJ, Hui YZ, Hubbell CL, Reid LD. Methylenedioxymethamphetamine’s capacity to establish place preferences and modify intake of an alcoholic beverage. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1990;37:633–8. - PubMed
-
- Callahan PM, Appel JB, Cunningham KA. Dopamine D1 and D2 mediation of the discriminative stimulus properties of d-amphetamine and cocaine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1990;103:50–55. - PubMed
-
- Callaway CW, Wing LL, Geyer MA. Serotonin release contributes to the locomotor stimulant effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990;254:456–64. - PubMed
-
- Carroll FI, Blough BE, Abraham P, Mills AC, Holleman JA, Wolckenhauer SA, Decker AM, Landavazo A, McElroy KT, Navarro HA, Gatch MB, Forster MJ. Synthesis and biological evaluation of bupropion analogues as potential pharmacotherapies for cocaine addiction. J Med Chem. 2009;52:6768–81. - PubMed
-
- Casale JF, Hays PA. Characterization of the “Methylenedioxy-2-aminoindans”. Microgram J. 2011;8:43–52.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

