Antiphospholipid antibody-induced miR-146a-3p drives trophoblast interleukin-8 secretion through activation of Toll-like receptor 8
- PMID: 27029214
- PMCID: PMC4941806
- DOI: 10.1093/molehr/gaw027
Antiphospholipid antibody-induced miR-146a-3p drives trophoblast interleukin-8 secretion through activation of Toll-like receptor 8
Abstract
Study question: What is the role of microRNAs (miRs) in antiphospholipid antibody (aPL)-induced trophoblast inflammation?
Summary answer: aPL-induced up-regulation of trophoblast miR-146a-3p is mediated by Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), and miR-146a-3p in turn drives the cells to secrete interleukin (IL)-8 by activating the RNA sensor, TLR8.
What is known already: Obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by circulating aPL and an increased risk of pregnancy complications. We previously showed that aPL recognizing beta2 glycoprotein I (β2GPI) elicit human first trimester trophoblast secretion of IL-8 by activating TLR4. Since some miRs control TLR responses, their regulation in trophoblast cells by aPL and functional role in the aPL-mediated inflammatory response was investigated. miRs can be released from cells via exosomes, and therefore, miR exosome expression was also examined. A panel of miRs was selected based on their involvement with TLR signaling: miR-9; miR-146a-5p and its isomiR, miR-146a-3p; miR-155, miR-210; and Let-7c. Since certain miRs can activate the RNA sensor, TLR8, this was also investigated.
Study design, size, duration: For in vitro studies, the human first trimester extravillous trophoblast cell line, HTR8 was studied. HTR8 cells transfected to express a TLR8 dominant negative (DN) were also used. Plasma was evaluated from pregnant women who have aPL, either with or without systemic lupus erythematous (SLE) (n = 39); SLE patients without aPL (n = 30); and healthy pregnant controls (n = 20).
Participants/materials, setting, methods: Trophoblast HTR8 wildtype and TLR8-DN cells were incubated with or without aPL (mouse anti-human β2GPI mAb) for 48-72 h. HTR8 cells were also treated with or without aPL in the presence and the absence of a TLR4 antagonist (lipopolysaccharide from Rhodobacter sphaeroides; LPS-RS), specific miR inhibitors or specific miR mimics. miR expression levels in trophoblast cells, trophoblast-derived exosomes and exosomes isolated from patient plasma were measured by qPCR. Trophoblast IL-8 secretion was measured by ELISA.
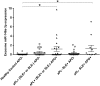
Main results and the role of chance: aPL significantly increased trophoblast cellular and exosome expression of miR-146a-5p, miR-146a-3p, miR-155 and miR-210. aPL-induced up-regulation of trophoblast miR-146a-5p, miR-146a-3p and miR-210, but not miR-155, was inhibited by the TLR4 antagonist, LPS-RS. While inhibition or overexpression of miR-146a-5p had no effect on aPL-induced trophoblast IL-8 secretion, miR-146a-3p inhibition significantly reduced this response. aPL-induced trophoblast IL-8 secretion was inhibited by the presence of the TLR8-DN. In the absence of aPL, transfection of trophoblast cells with a miR-146a-3p mimic significantly increased IL-8 secretion and this was inhibited by the presence of the TLR8-DN. Patients with aPL and adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs) expressed significantly higher levels of circulating miR-146a-3p compared with healthy pregnant controls with no pregnancy complications (P < 0.05).
Limitations, reasons for caution: While the enrichment of miR-146a-3p in trophoblast-derived exosomes support the role of this miR acting in a paracrine or endocrine manner through exosome delivery, this has not been demonstrated. However, miR-146a-3p may also exert its pro-inflammatory effect intracellularly within the same trophoblast cell targeted by aPL.
Wider implications of the findings: These findings provide a novel mechanism of trophoblast inflammation through miRs activating RNA-sensing receptors. Furthermore, circulating exosomal-associated miR-146a-3p in APS patients may serve clinically as a biomarker for related APOs.
Study funding/competing interests: This study was supported in part by grants from the American Heart Association (#10GRNT3640032 to V.M.A.), the March of Dimes Foundation (Gene Discovery and Translational Research Grant #6-FY12-255 to V.M.A.), NICHD, NIH (R01HD049446 to V.M.A.), the Gina M. Finzi Memorial Student Summer Fellowship from the Lupus Foundation of America (to S.M.G.), and the Yale University School of Medicine Medical Student Fellowship (to S.M.G.). The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Trial registration number: N/A.
Keywords: MicroRNA; Toll-like receptor; antiphospholipid antibody; antiphospholipid syndrome; exosome; inflammation; lupus; placenta; pregnancy; trophoblast.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Albert CR, Schlesinger WJ, Viall CA, Mulla MJ, Brosens JJ, Chamley LW, Abrahams VM. Effect of hydroxychloroquine on antiphospholipid antibody-induced changes in first trimester trophoblast function. Am J Reprod Immunol 2014;71:154–164. - PubMed
-
- Berman J, Girardi G, Salmon JE. TNF-alpha is a critical effector and a target for therapy in antiphospholipid antibody-induced pregnancy loss. J Immunol 2005;174:485–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

