Enzymatic properties, evidence for in vivo expression, and intracellular localization of shewasin D, the pepsin homolog from Shewanella denitrificans
- PMID: 27029611
- PMCID: PMC4814920
- DOI: 10.1038/srep23869
Enzymatic properties, evidence for in vivo expression, and intracellular localization of shewasin D, the pepsin homolog from Shewanella denitrificans
Abstract
The widespread presence of pepsin-like enzymes in eukaryotes together with their relevance in the control of multiple biological processes is reflected in the large number of studies published so far for this family of enzymes. By contrast, pepsin homologs from bacteria have only recently started to be characterized. The work with recombinant shewasin A from Shewanella amazonensis provided the first documentation of this activity in prokaryotes. Here we extend our studies to shewasin D, the pepsin homolog from Shewanella denitrificans, to gain further insight into this group of bacterial peptidases that likely represent ancestral versions of modern eukaryotic pepsin-like enzymes. We demonstrate that the enzymatic properties of recombinant shewasin D are strongly reminiscent of eukaryotic pepsin homologues. We determined the specificity preferences of both shewasin D and shewasin A using proteome-derived peptide libraries and observed remarkable similarities between both shewasins and eukaryotic pepsins, in particular with BACE-1, thereby confirming their phylogenetic proximity. Moreover, we provide first evidence of expression of active shewasin D in S. denitrificans cells, confirming its activity at acidic pH and inhibition by pepstatin. Finally, our results revealed an unprecedented localization for a family A1 member by demonstrating that native shewasin D accumulates preferentially in the cytoplasm.
Figures
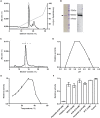
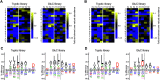


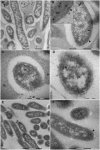
Similar articles
-
Shewasin A, an active pepsin homolog from the bacterium Shewanella amazonensis.FEBS J. 2011 Sep;278(17):3177-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08243.x. Epub 2011 Aug 11. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21749650
-
Purification and characterization of pepsins A1 and A2 from the Antarctic rock cod Trematomus bernacchii.FEBS J. 2007 Dec;274(23):6152-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.06136.x. Epub 2007 Nov 1. FEBS J. 2007. PMID: 17976195 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering the residual side chains of HAP phytases to improve their pepsin resistance and catalytic efficiency.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 10;7:42133. doi: 10.1038/srep42133. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28186144 Free PMC article.
-
A history of pepsin and related enzymes.Q Rev Biol. 2002 Jun;77(2):127-47. doi: 10.1086/340729. Q Rev Biol. 2002. PMID: 12089768 Review.
-
Specificity and mechanism of pepsin action on synthetic substrates.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;95:131-40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0719-9_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977. PMID: 339686 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The Retropepsin-Type Protease APRc as a Novel Ig-Binding Protein and Moonlighting Immune Evasion Factor of Rickettsia.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0305921. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03059-21. Epub 2021 Dec 7. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34872352 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective analysis of mucosal microbiome-metabonome interactions in colorectal cancer using a combined MAS 1HNMR and metataxonomic strategy.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 21;7(1):8979. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08150-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28827587 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Borosin Catalytic Strategies and Function through Bioinformatic Profiling.ACS Chem Biol. 2024 May 17;19(5):1116-1124. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.4c00066. Epub 2024 May 2. ACS Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38695893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neil D., Rawlings J. & Alan J.. Barrett Chapter 1 - Introduction: Aspartic and Glutamic Peptidases and Their Clans in Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes (ed. Neil D., Salvesen R.) 3–19 (Academic Press, 2013).
-
- Alexander, Wlodawer, Alla, N. G. Gustchina & Michael. James Chapter 2 - Catalytic Pathways of Aspartic Peptidases, in Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes (ed. Neil D., Salvesen R.) 19–26 (Academic Press, 2013).
-
- Ido E. et al. “Kinetic studies of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease and its active-site hydrogen bond mutant A28S”. J. Biol. Chem. 266(36), 24359 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Simoes I. et al. “Shewasin A, an active pepsin homolog from the bacterium Shewanella amazonensis”. FEBS J. 278(17), 3177 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

