Protein Kinase D and Gβγ Subunits Mediate Agonist-evoked Translocation of Protease-activated Receptor-2 from the Golgi Apparatus to the Plasma Membrane
- PMID: 27030010
- PMCID: PMC4900274
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.710681
Protein Kinase D and Gβγ Subunits Mediate Agonist-evoked Translocation of Protease-activated Receptor-2 from the Golgi Apparatus to the Plasma Membrane
Abstract
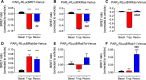
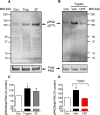
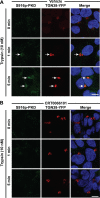
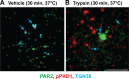
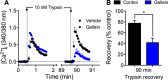
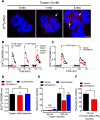
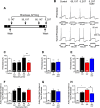
Agonist-evoked endocytosis of G protein-coupled receptors has been extensively studied. The mechanisms by which agonists stimulate mobilization and plasma membrane translocation of G protein-coupled receptors from intracellular stores are unexplored. Protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) traffics to lysosomes, and sustained protease signaling requires mobilization and plasma membrane trafficking of PAR2 from Golgi stores. We evaluated the contribution of protein kinase D (PKD) and Gβγ to this process. In HEK293 and KNRK cells, the PAR2 agonists trypsin and 2-furoyl-LIGRLO-NH2 activated PKD in the Golgi apparatus, where PKD regulates protein trafficking. PAR2 activation induced translocation of Gβγ, a PKD activator, to the Golgi apparatus, determined by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer between Gγ-Venus and giantin-Rluc8. Inhibitors of PKD (CRT0066101) and Gβγ (gallein) prevented PAR2-stimulated activation of PKD. CRT0066101, PKD1 siRNA, and gallein all inhibited recovery of PAR2-evoked Ca(2+) signaling. PAR2 with a photoconvertible Kaede tag was expressed in KNRK cells to examine receptor translocation from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane. Irradiation of the Golgi region (405 nm) induced green-red photo-conversion of PAR2-Kaede. Trypsin depleted PAR2-Kaede from the Golgi apparatus and repleted PAR2-Kaede at the plasma membrane. CRT0066101 inhibited PAR2-Kaede translocation to the plasma membrane. CRT0066101 also inhibited sustained protease signaling to colonocytes and nociceptive neurons that naturally express PAR2 and mediate protease-evoked inflammation and nociception. Our results reveal a major role for PKD and Gβγ in agonist-evoked mobilization of intracellular PAR2 stores that is required for sustained signaling by extracellular proteases.
Keywords: 7-helix receptor; Golgi; protein kinase D (PKD); protein trafficking (Golgi); receptor desensitization.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- McConalogue K., Déry O., Lovett M., Wong H., Walsh J. H., Grady E. F., and Bunnett N. W. (1999) Substance P-induced trafficking of β-arrestins. The role of β-arrestins in endocytosis of the neurokinin-1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 16257–16268 - PubMed
-
- Déry O., Thoma M. S., Wong H., Grady E. F., and Bunnett N. W. (1999) Trafficking of proteinase-activated receptor-2 and β-arrestin-1 tagged with green fluorescent protein. β-Arrestin-dependent endocytosis of a proteinase receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 18524–18535 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

