Neutral glycans from sandfish skin can reduce friction of polymers
- PMID: 27030038
- PMCID: PMC4843684
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2016.0103
Neutral glycans from sandfish skin can reduce friction of polymers
Abstract
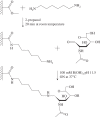
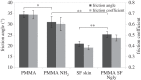
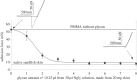
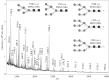
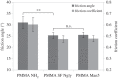
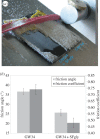
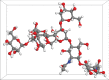
The lizardScincus scincus, also known as sandfish, can move through aeolian desert sand in a swimming-like manner. A prerequisite for this ability is a special integument, i.e. scales with a very low friction for sand and a high abrasion resistance. Glycans in the scales are causally related to the low friction. Here, we analysed the glycans and found that neutral glycans with five to nine mannose residues are important. If these glycans were covalently bound to acrylic polymers like poly(methyl methacrylate) or acrylic car coatings at a density of approximately one molecule per 4 nm², friction for and adhesion of sand particles could be reduced to levels close to those observed with sandfish scales. This was also found true, if the glycans were isolated from sources other than sandfish scales like plants such as almonds or mistletoe. We speculate that these neutral glycans act as low density spacers separating sand particles from the dense scales thereby reducing van der Waals forces.
Keywords: Scincus; integument; mannose; mass spectroscopy; sand swimming.
© 2016 The Authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the microscopic tribological properties of sandfish (Scincus scincus) scales by atomic force microscopy.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2018 Oct 2;9:2618-2627. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.9.243. eCollection 2018. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30416912 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental interaction influences muscle activation strategy during sand-swimming in the sandfish lizard Scincus scincus.J Exp Biol. 2013 Jan 15;216(Pt 2):260-74. doi: 10.1242/jeb.070482. J Exp Biol. 2013. PMID: 23255193
-
Investigating the locomotion of the sandfish in desert sand using NMR-imaging.PLoS One. 2008 Oct 1;3(10):e3309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003309. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18836551 Free PMC article.
-
Undulatory swimming in sand: subsurface locomotion of the sandfish lizard.Science. 2009 Jul 17;325(5938):314-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1172490. Science. 2009. PMID: 19608917
-
Adaptation to life in aeolian sand: how the sandfish lizard, Scincus scincus, prevents sand particles from entering its lungs.J Exp Biol. 2016 Nov 15;219(Pt 22):3597-3604. doi: 10.1242/jeb.138107. J Exp Biol. 2016. PMID: 27852763 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Simulation and Structural Analysis of a Flexible Coupling Bionic Desorption Mechanism Based on the Engineering Discrete Element Method.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 Apr 8;9(4):224. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9040224. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667235 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the microscopic tribological properties of sandfish (Scincus scincus) scales by atomic force microscopy.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2018 Oct 2;9:2618-2627. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.9.243. eCollection 2018. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30416912 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological study of the integument and corporal skeletal muscles of two psammophilous members of Scincidae (Scincus scincus and Eumeces schneideri).J Morphol. 2021 Feb;282(2):230-246. doi: 10.1002/jmor.21298. Epub 2020 Nov 9. J Morphol. 2021. PMID: 33165963 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorinated Galactoses Inhibit Galactose-1-Phosphate Uridyltransferase and Metabolically Induce Galactosemia-like Phenotypes in HEK-293 Cells.Cells. 2020 Mar 3;9(3):607. doi: 10.3390/cells9030607. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32138379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garsault FAP. 1764. Les figures des plantes et animaux d'usage en medecine, d́ecrits dans la Matiere Medicale, p. 85. Paris: Geoffroy Medecin.
-
- Arnold EN, Leviton AE. 1977. A revision of the lizard genus Scincus (Reptilia: Scincidae). Bull. Br. Mus. Nat. Hist. Zool. 31, 189–248.
-
- Hartmann UK. 1989. Beitrag zur Biologie des Apothekerskinks Scincus scincus. Herpetofauna 11, 17–39.
-
- Rechenberg I, El Khyari AR. 2004. Reibung und Verschleiß am Sandfisch der Sahara. See http://www.bionik.tu-berlin.de/institut/festo04.pdf (accessed 15 January 2015).
-
- Baumgartner W, Saxe F, Weth A, Hajas D, Sigumonrong D, Emmerlich J, Singheiser M, Böhme W, Schneider JM. 2007. The sandfish's skin: morphology, chemistry and reconstruction. J. Bionic Eng. 4, 1–9. (10.1016/S1672-6529(07)60006-7) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

