Carglumic acid enhances rapid ammonia detoxification in classical organic acidurias with a favourable risk-benefit profile: a retrospective observational study
- PMID: 27030250
- PMCID: PMC4815113
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-016-0406-2
Carglumic acid enhances rapid ammonia detoxification in classical organic acidurias with a favourable risk-benefit profile: a retrospective observational study
Abstract
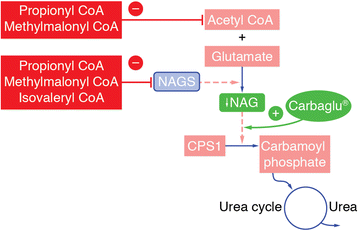
Background: Isovaleric aciduria (IVA), propionic aciduria (PA) and methylmalonic aciduria (MMA) are inherited organic acidurias (OAs) in which impaired organic acid metabolism induces hyperammonaemia arising partly from secondary deficiency of N-acetylglutamate (NAG) synthase. Rapid reduction in plasma ammonia is required to prevent neurological complications. This retrospective, multicentre, open-label, uncontrolled, phase IIIb study evaluated the efficacy and safety of carglumic acid, a synthetic structural analogue of NAG, for treating hyperammonaemia during OA decompensation.
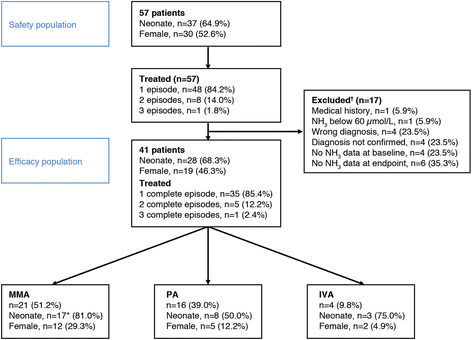
Methods: Eligible patients had confirmed OA and hyperammonaemia (plasma NH3 > 60 μmol/L) in ≥1 decompensation episode treated with carglumic acid (dose discretionary, mean (SD) first dose 96.3 (73.8) mg/kg). The primary outcome was change in plasma ammonia from baseline to endpoint (last available ammonia measurement at ≤18 hours after the last carglumic acid administration, or on Day 15) for each episode. Secondary outcomes included clinical response and safety.
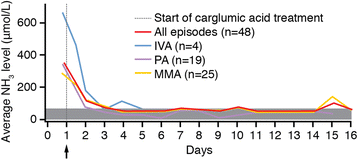
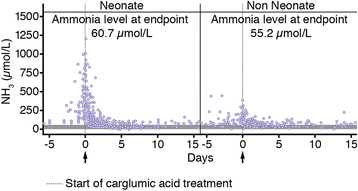
Results: The efficacy population (received ≥1 dose of study drug and had post-baseline measurements) comprised 41 patients (MMA: 21, PA: 16, IVA: 4) with 48 decompensation episodes (MMA: 25, PA: 19, IVA: 4). Mean baseline plasma ammonia concentration was 468.3 (±365.3) μmol/L in neonates (29 episodes) and 171.3 (±75.7) μmol/L in non-neonates (19 episodes). At endpoint the mean plasma NH3 concentration was 60.7 (±36.5) μmol/L in neonates and 55.2 (±21.8) μmol/L in non-neonates. Median time to normalise ammonaemia was 38.4 hours in neonates vs 28.3 hours in non-neonates and was similar between OA subgroups (MMA: 37.5 hours, PA: 36.0 hours, IVA: 40.5 hours). Median time to ammonia normalisation was 1.5 and 1.6 days in patients receiving and not receiving concomitant scavenger therapy, respectively. Although patients receiving carglumic acid with scavengers had a greater reduction in plasma ammonia, the endpoint ammonia levels were similar with or without scavenger therapy. Clinical symptoms improved with therapy. Twenty-five of 57 patients in the safety population (67 episodes) experienced AEs, most of which were not drug-related. Overall, carglumic acid seems to have a good safety profile for treating hyperammonaemia during OA decompensation.
Conclusion: Carglumic acid when used with or without ammonia scavengers, is an effective treatment for restoration of normal plasma ammonia concentrations in hyperammonaemic episodes in OA patients.
Keywords: Carglumic acid; Hyperammonaemia; OA decompensation episodes; Organic acidurias (OAs).
Figures
References
-
- Dionisi-Vici C, Deodato F, Röschinger W, Rhead W, Wilcken B. ‘Classical’ organic acidurias, propionic aciduria, methylmalonic aciduria and isovaleric aciduria: long-term outcome and effects of expanded newborn screening using tandem mass spectrometry. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2006;29:383–9. doi: 10.1007/s10545-006-0278-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Seashore MR. The Organic Acidemias. An Overview. In Gene Reviews 2009. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1134/. Accessed 3 Oct 2015.
-
- Coude FX, Ogier H, Grimber G, Parvy P, Pham Dinh D, Charpentier C, Saudubray JM. Correlation between blood ammonia concentration and organic acid accumulation in isovaleric and propionic acidemia. Pediatrics. 1982;69:115–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

