Emancipating Chlamydia: Advances in the Genetic Manipulation of a Recalcitrant Intracellular Pathogen
- PMID: 27030552
- PMCID: PMC4867370
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00071-15
Emancipating Chlamydia: Advances in the Genetic Manipulation of a Recalcitrant Intracellular Pathogen
Abstract
Chlamydia species infect millions of individuals worldwide and are important etiological agents of sexually transmitted disease, infertility, and blinding trachoma. Historically, the genetic intractability of this intracellular pathogen has hindered the molecular dissection of virulence factors contributing to its pathogenesis. The obligate intracellular life cycle of Chlamydia and restrictions on the use of antibiotics as selectable markers have impeded the development of molecular tools to genetically manipulate these pathogens. However, recent developments in the field have resulted in significant gains in our ability to alter the genome of Chlamydia, which will expedite the elucidation of virulence mechanisms. In this review, we discuss the challenges affecting the development of molecular genetic tools for Chlamydia and the work that laid the foundation for recent advancements in the genetic analysis of this recalcitrant pathogen.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


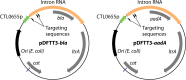
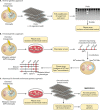
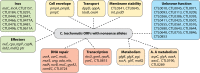
References
-
- Harris SR, Clarke IN, Seth-Smith HM, Solomon AW, Cutcliffe LT, Marsh P, Skilton RJ, Holland MJ, Mabey D, Peeling RW, Lewis DA, Spratt BG, Unemo M, Persson K, Bjartling C, Brunham R, de Vries HJ, Morre SA, Speksnijder A, Bebear CM, Clerc M, de Barbeyrac B, Parkhill J, Thomson NR. 2012. Whole-genome analysis of diverse Chlamydia trachomatis strains identifies phylogenetic relationships masked by current clinical typing. Nat Genet 44:413–419. doi: 10.1038/ng.2214. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peipert JF. 2003. Clinical practice. Genital chlamydial infections. N Engl J Med 349:2424–2430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

