Conformational Modeling of Continuum Structures in Robotics and Structural Biology: A Review
- PMID: 27030786
- PMCID: PMC4809027
- DOI: 10.1080/01691864.2015.1052848
Conformational Modeling of Continuum Structures in Robotics and Structural Biology: A Review
Abstract
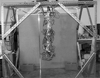
Hyper-redundant (or snakelike) manipulators have many more degrees of freedom than are required to position and orient an object in space. They have been employed in a variety of applications ranging from search-and-rescue to minimally invasive surgical procedures, and recently they even have been proposed as solutions to problems in maintaining civil infrastructure and the repair of satellites. The kinematic and dynamic properties of snakelike robots are captured naturally using a continuum backbone curve equipped with a naturally evolving set of reference frames, stiffness properties, and mass density. When the snakelike robot has a continuum architecture, the backbone curve corresponds with the physical device itself. Interestingly, these same modeling ideas can be used to describe conformational shapes of DNA molecules and filamentous protein structures in solution and in cells. This paper reviews several classes of snakelike robots: (1) hyper-redundant manipulators guided by backbone curves; (2) flexible steerable needles; and (3) concentric tube continuum robots. It is then shown how the same mathematical modeling methods used in these robotics contexts can be used to model molecules such as DNA. All of these problems are treated in the context of a common mathematical framework based on the differential geometry of curves, continuum mechanics, and variational calculus. Both coordinate-dependent Euler-Lagrange formulations and coordinate-free Euler-Poincaré approaches are reviewed.
Figures
References
-
- Alterovitz R, Lim A, Goldberg K, Chirikjian GS, Okamura AM. Steering flexible needles under Markov motion uncertainty; Proc. IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems; 2005. Aug, pp. 120–125.
-
- Balaeff A, Mahadevan L, Schulten K. Modeling DNA loops using the theory of elasticity. 2003 E-print archive arXiv.org ( http://arxiv.org/abs/physics/0301006. - PubMed
-
- Balaeff A, Mahadevan L, Schulten K. Structural basis for cooperative DNA binding by CAP and Lac Repressor. Structure. 2004;12:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Benham CJ. Elastic Model of the Large-Scale Structure of Duplex DNA. Biopolymers. 1979;18(3):609–623. - PubMed
-
- Benham CJ, Mielke SP. DNA mechanics. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 2005;7:21–53. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources