Impact of similarity threshold on the topology of molecular similarity networks and clustering outcomes
- PMID: 27030802
- PMCID: PMC4812625
- DOI: 10.1186/s13321-016-0127-5
Impact of similarity threshold on the topology of molecular similarity networks and clustering outcomes
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Impact of similarity threshold on the topology of molecular similarity networks and clustering outcomes.J Cheminform. 2016 May 20;8:28. doi: 10.1186/s13321-016-0140-8. eCollection 2016. J Cheminform. 2016. PMID: 27213018 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Complex network theory based methods and the emergence of "Big Data" have reshaped the terrain of investigating structure-activity relationships of molecules. This change gave rise to new methods which need to face an important challenge, namely: how to restructure a large molecular dataset into a network that best serves the purpose of the subsequent analyses. With special focus on network clustering, our study addresses this open question by proposing a data transformation method and a clustering framework.
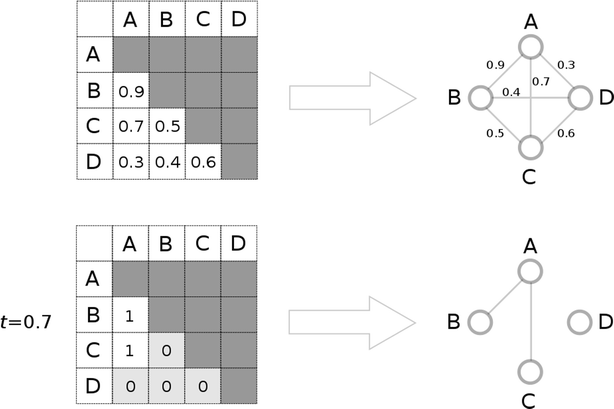
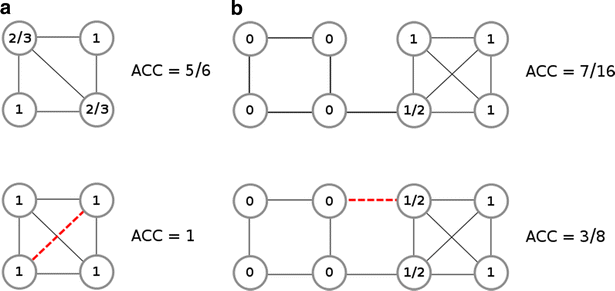
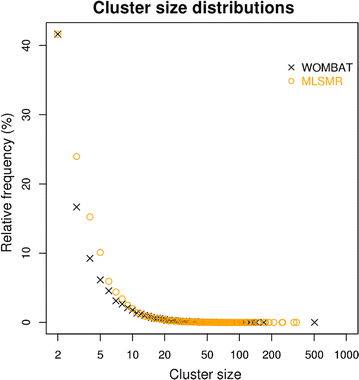
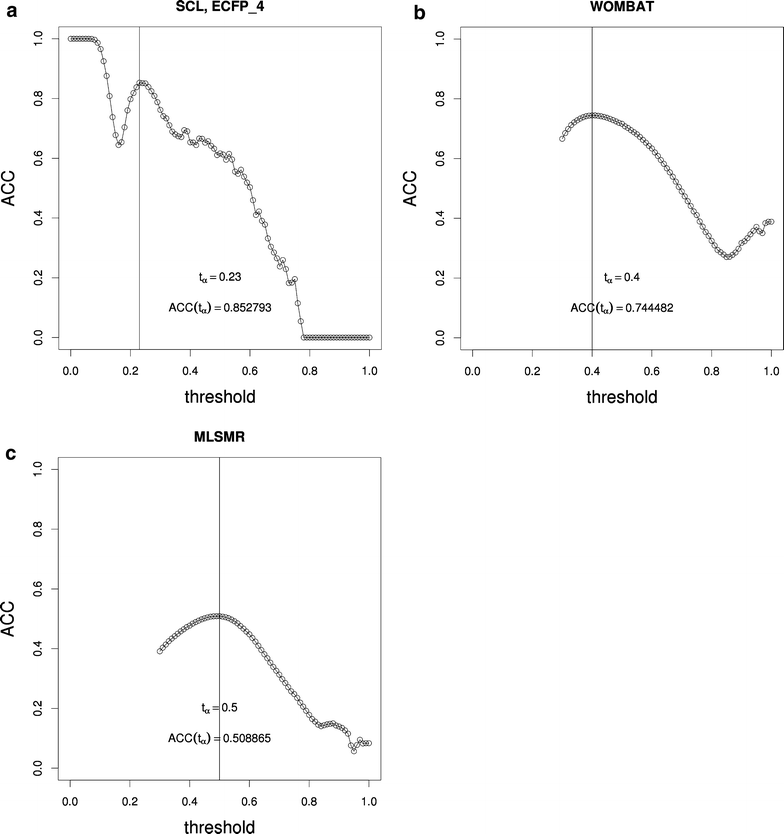
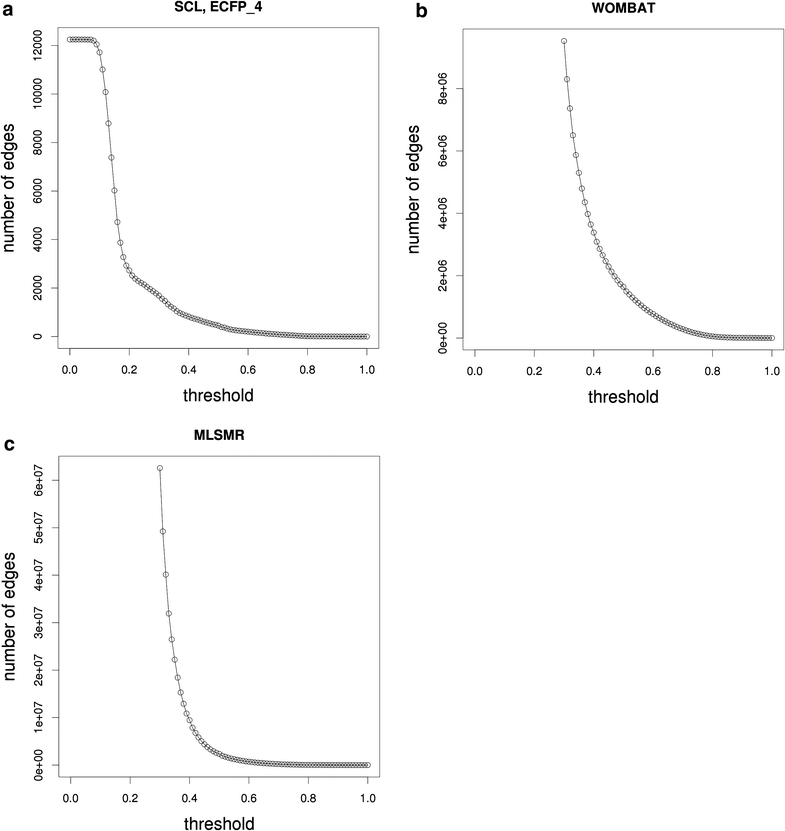
Results: Using the WOMBAT and PubChem MLSMR datasets we investigated the relation between varying the similarity threshold applied on the similarity matrix and the average clustering coefficient of the emerging similarity-based networks. These similarity networks were then clustered with the InfoMap algorithm. We devised a systematic method to generate so-called "pseudo-reference" clustering datasets which compensate for the lack of large-scale reference datasets. With help from the clustering framework we were able to observe the effects of varying the similarity threshold and its consequence on the average clustering coefficient and the clustering performance.
Conclusions: We observed that the average clustering coefficient versus similarity threshold function can be characterized by the presence of a peak that covers a range of similarity threshold values. This peak is preceded by a steep decline in the number of edges of the similarity network. The maximum of this peak is well aligned with the best clustering outcome. Thus, if no reference set is available, choosing the similarity threshold associated with this peak would be a near-ideal setting for the subsequent network cluster analysis. The proposed method can be used as a general approach to determine the appropriate similarity threshold to generate the similarity network of large-scale molecular datasets.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

