Ubiquitin-specific protease 22 is a deubiquitinase of CCNB1
- PMID: 27030811
- PMCID: PMC4809424
- DOI: 10.1038/celldisc.2015.28
Ubiquitin-specific protease 22 is a deubiquitinase of CCNB1
Abstract
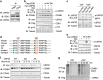
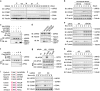
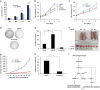
The elevated level of CCNB1 indicates more aggressive cancer and poor prognosis. However, the factors that cause CCNB1 upregulation remain enigmatic. Herein, we identify USP22 as a CCNB1 interactor and discover that both USP22 and CCNB1 are dramatically elevated with a strong positive correlation in colon cancer tissues. USP22 stabilizes CCNB1 by antagonizing proteasome-mediated degradation in a cell cycle-specific manner. Phosphorylation of USP22 by CDK1 enhances its activity in deubiquitinating CCNB1. The ubiquitin ligase anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) targets USP22 for degradation by using the substrate adapter CDC20 during cell exit from M phase, presumably allowing CCNB1 degradation. Finally, we discover that USP22 knockdown leads to slower cell growth and reduced tumor size. Our study demonstrates that USP22 is a CCNB1 deubiquitinase, suggesting that targeting USP22 might be an effective approach to treat cancers with elevated CCNB1 expression.
Keywords: APC8; CCNB1; USP22; cell cycle; tumorigenesis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ubiquitin-specific protease 22 acts as an oncoprotein to maintain glioma malignancy through deubiquitinating B cell-specific Moloney murine leukemia virus integration site 1 for stabilization.Cancer Sci. 2018 Jul;109(7):2199-2210. doi: 10.1111/cas.13646. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29788550 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin-specific peptidase 22 is a deubiquitinase of CD73 in breast cancer cells.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Dec 15;12(12):5564-5575. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36628293 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor promotes melanoma metastasis through ubiquitin-specific peptidase 22-mediated integrins upregulation.Cancer Lett. 2024 Nov 1;604:217196. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217196. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Cancer Lett. 2024. PMID: 39222676
-
Cdc20 protein contains a destruction-box but, unlike Clb2, its proteolysisis not acutely dependent on the activity of anaphase-promoting complex.Eur J Biochem. 2000 Jan;267(2):434-49. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01014.x. Eur J Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10632713
-
Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 22 Regulates Histone H2B Mono-Ubiquitination and Exhibits Both Oncogenic and Tumor Suppressor Roles in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2017 Dec 6;9(12):167. doi: 10.3390/cancers9120167. Cancers (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29210986 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rad50 promotes ovarian cancer progression through NF-κB activation.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Dec;25(23):10961-10972. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17017. Epub 2021 Nov 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34734468 Free PMC article.
-
A chromatin-focused CRISPR screen identifies USP22 as a barrier to somatic cell reprogramming.Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 18;8(1):454. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07899-y. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40102626 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into APC/C: from cellular function to diseases and therapeutics.Cell Div. 2016 Jul 13;11:9. doi: 10.1186/s13008-016-0021-6. eCollection 2016. Cell Div. 2016. PMID: 27418942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-specific protease 22 is critical to in vivo angiogenesis, growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Dec 16;17(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0480-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31842906 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role of Deubiquitinating Enzymes (DUBs) in Melanoma Pathogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 11;14(14):3371. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143371. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Glinsky GV . Genomic models of metastatic cancer: functional analysis of death-from-cancer signature genes reveals aneuploid, anoikis-resistant, metastasis-enabling phenotype with altered cell cycle control and activated Polycomb Group (PcG) protein chromatin silencing pathway. Cell cycle 2006; 5: 1208–1216. - PubMed
-
- Nixon VL , Levasseur M , McDougall A , Jones KT . Ca(2+) oscillations promote APC/C-dependent cyclin B1 degradation during metaphase arrest and completion of meiosis in fertilizing mouse eggs. Curr Biol 2002; 12: 746–750. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

