Functional lumen imaging probe: The FLIP side of esophageal disease
- PMID: 27030931
- PMCID: PMC5555117
- DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000272
Functional lumen imaging probe: The FLIP side of esophageal disease
Abstract
Purpose of review: The aim of this review is to summarize use of the functional lumen imaging probe (FLIP) for the evaluation and management of esophageal diseases.
Recent findings: The FLIP utilizes high-resolution impedance planimetry to evaluate the functional geometry and cross-sectional area/pressure relationship (i.e. distensibility) of the esophageal sphincters and body. Recent studies have reported the potential utility of FLIP to evaluate esophageal diseases, such as achalasia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and eosinophilic esophagitis.
Summary: Esophageal distensibility measures provided by the FLIP will add to our understanding of the contribution of esophageal mechanical properties to esophageal symptoms and function. Application of the FLIP in clinical practice complements the diagnostic evaluation of esophageal function and may also be a valuable tool to help direct and target clinical management of esophageal diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
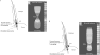
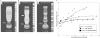

Similar articles
-
Use of the Functional Lumen Imaging Probe in Clinical Esophagology.Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 Nov;115(11):1786-1796. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000773. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33156096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Impedance Planimetry in the Evaluation of Esophageal Disorders.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2017 Feb;19(2):7. doi: 10.1007/s11894-017-0544-2. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28220362 Review.
-
The functional lumen imaging probe in gastrointestinal disorders: the past, present, and future.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020 Dec;1482(1):16-25. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14463. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020. PMID: 32814368 Review.
-
Functional Lumen Imaging Probe Panometry.Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2025 Jul;35(3):571-585. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2025.01.007. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2025. PMID: 40412991 Review.
-
EndoFLIP in the Esophagus: Assessing Sphincter Function, Wall Stiffness, and Motility to Guide Treatment.Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2020 Sep;49(3):427-435. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2020.04.002. Epub 2020 Jun 14. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 32718562 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of preoperative, intraoperative, and follow-up functional luminal imaging probe measurements in patients undergoing myotomy for achalasia.Gastrointest Endosc. 2021 Sep;94(3):509-514. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.02.031. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021. PMID: 33662363 Free PMC article.
-
A deep-learning-based unsupervised model on esophageal manometry using variational autoencoder.Artif Intell Med. 2021 Feb;112:102006. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2020.102006. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Artif Intell Med. 2021. PMID: 33581826 Free PMC article.
-
Use of the Functional Lumen Imaging Probe in Clinical Esophagology.Am J Gastroenterol. 2020 Nov;115(11):1786-1796. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000773. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33156096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subjective Assessment of the Pyloric Sphincter During Endoscopy and Its Correlation with FLIP Panometry.Dig Dis Sci. 2025 Jun 27. doi: 10.1007/s10620-025-09127-3. Online ahead of print. Dig Dis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40579596
-
Experience-based expert consensus on the intra-operative usage of the Endoflip impedance planimetry system.Surg Endosc. 2021 Jun;35(6):2731-2742. doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-07704-3. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Surg Endosc. 2021. PMID: 32556758
References
-
- Pandolfino JE, Shi G, Trueworthy B, et al. Esophagogastric junction opening during relaxation distinguishes nonhernia reflux patients, hernia patients, and normal subjects. Gastroenterology. 2003;125(4):1018–24. - PubMed
-
- Rao SS, Hayek B, Summers RW. Impedance planimetry: an integrated approach for assessing sensory, active, and passive biomechanical properties of the human esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90(3):431–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

