Expression of Leukemia-Associated Nup98 Fusion Proteins Generates an Aberrant Nuclear Envelope Phenotype
- PMID: 27031510
- PMCID: PMC4816316
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152321
Expression of Leukemia-Associated Nup98 Fusion Proteins Generates an Aberrant Nuclear Envelope Phenotype
Abstract
Chromosomal translocations involving the nucleoporin NUP98 have been described in several hematopoietic malignancies, in particular acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In the resulting chimeric proteins, Nup98's N-terminal region is fused to the C-terminal region of about 30 different partners, including homeodomain (HD) transcription factors. While transcriptional targets of distinct Nup98 chimeras related to immortalization are relatively well described, little is known about other potential cellular effects of these fusion proteins. By comparing the sub-nuclear localization of a large number of Nup98 fusions with HD and non-HD partners throughout the cell cycle we found that while all Nup98 chimeras were nuclear during interphase, only Nup98-HD fusion proteins exhibited a characteristic speckled appearance. During mitosis, only Nup98-HD fusions were concentrated on chromosomes. Despite the difference in localization, all tested Nup98 chimera provoked morphological alterations in the nuclear envelope (NE), in particular affecting the nuclear lamina and the lamina-associated polypeptide 2α (LAP2α). Importantly, such aberrations were not only observed in transiently transfected HeLa cells but also in mouse bone marrow cells immortalized by Nup98 fusions and in cells derived from leukemia patients harboring Nup98 fusions. Our findings unravel Nup98 fusion-associated NE alterations that may contribute to leukemogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


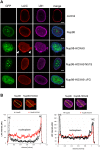
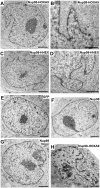
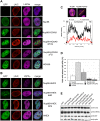
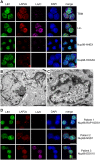
Similar articles
-
Nup98-homeodomain fusions interact with endogenous Nup98 during interphase and localize to kinetochores and chromosome arms during mitosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 May 1;21(9):1585-96. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-07-0561. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20237156 Free PMC article.
-
A cryptic translocation leading to NUP98-PHF23 fusion in AML.Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2016 Dec;29(4):320-323. doi: 10.1016/j.beha.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2016. PMID: 27890253 Review.
-
Leukemogenic mechanisms and targets of a NUP98/HHEX fusion in acute myeloid leukemia.Blood. 2008 Jun 15;111(12):5672-82. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-108175. Epub 2008 Apr 3. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18388181
-
Major form of NUP98/HOXC11 fusion in adult AML with t(11;12)(p15;q13) translocation exhibits aberrant trans-regulatory activity.Leukemia. 2003 Sep;17(9):1858-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2403036. Leukemia. 2003. PMID: 12970787
-
NUP98 fusion in human leukemia: dysregulation of the nuclear pore and homeodomain proteins.Int J Hematol. 2005 Jul;82(1):21-7. doi: 10.1532/IJH97.04160. Int J Hematol. 2005. PMID: 16105755 Review.
Cited by
-
Oncogenic fusion proteins and their role in three-dimensional chromatin structure, phase separation, and cancer.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2022 Jun;74:101901. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2022.101901. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2022. PMID: 35427897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The phenylalanine-and-glycine repeats of NUP98 oncofusions form condensates that selectively partition transcriptional coactivators.Mol Cell. 2025 Feb 20;85(4):708-725.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.12.026. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Mol Cell. 2025. PMID: 39922194
-
Tuning between Nuclear Organization and Functionality in Health and Disease.Cells. 2023 Feb 23;12(5):706. doi: 10.3390/cells12050706. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disclosing the Interactome of Leukemogenic NUP98-HOXA9 and SET-NUP214 Fusion Proteins Using a Proteomic Approach.Cells. 2020 Jul 10;9(7):1666. doi: 10.3390/cells9071666. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32664447 Free PMC article.
-
Phase separation drives aberrant chromatin looping and cancer development.Nature. 2021 Jul;595(7868):591-595. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03662-5. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Nature. 2021. PMID: 34163069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fahrenkrog B. Nucleoporin gene fusions and hematopoietic malignancies. New Journal of Science. 2014;Article ID 468306:1–18. 10.1155/2014/468306 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

