An Ultrastructural and Immunohistochemical Analysis of the Outer Plexiform Layer of the Retina of the European Silver Eel (Anguilla anguilla L)
- PMID: 27032102
- PMCID: PMC4816530
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152967
An Ultrastructural and Immunohistochemical Analysis of the Outer Plexiform Layer of the Retina of the European Silver Eel (Anguilla anguilla L)
Abstract
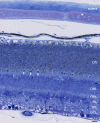
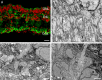
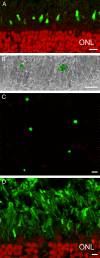
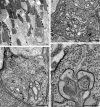
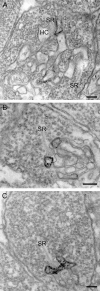
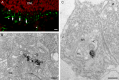
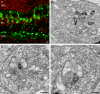
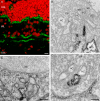
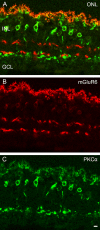
Here we studied the ultrastructural organization of the outer retina of the European silver eel, a highly valued commercial fish species. The retina of the European eel has an organization very similar to most vertebrates. It contains both rod and cone photoreceptors. Rods are abundantly present and immunoreactive for rhodopsin. Cones are sparsely present and only show immunoreactivity for M-opsin and not for L-, S- or UV-cone opsins. As in all other vertebrate retinas, Müller cells span the width of the retina. OFF-bipolar cells express the ionotropic glutamate receptor GluR4 and ON-bipolar cells, as identified by their PKCα immunoreactivity, express the metabotropic receptor mGluR6. Both the ON- and the OFF-bipolar cell dendrites innervate the cone pedicle and rod spherule. Horizontal cells are surrounded by punctate Cx53.8 immunoreactivity indicating that the horizontal cells are strongly electrically coupled by gap-junctions. Connexin-hemichannels were found at the tips of the horizontal cell dendrites invaginating the photoreceptor synapse. Such hemichannels are implicated in the feedback pathway from horizontal cells to cones. Finally, horizontal cells are surrounded by tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity, illustrating a strong dopaminergic input from interplexiform cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and localization of an immunoreactive AMPA-type glutamate receptor subunit (GluR4) with respect to identified photoreceptor synapses in the outer plexiform layer of goldfish retina.J Neurocytol. 1997 Oct;26(10):651-66. doi: 10.1023/a:1018597811439. J Neurocytol. 1997. PMID: 9368879
-
Immunocytochemical analysis of photoreceptors in the tiger salamander retina.Vision Res. 2009 Jan;49(1):64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2008.09.031. Epub 2008 Nov 25. Vision Res. 2009. PMID: 18977238 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal fine structure in the European eel Anguilla anguilla. VIII. Photoreceptors of the sexually mature silver eel stage.Anat Anz. 1988;167(1):1-10. Anat Anz. 1988. PMID: 3189854
-
The involvement of glutamate-gated channels in negative feedback from horizontal cells to cones.Prog Brain Res. 2005;147:219-29. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(04)47017-4. Prog Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15581709 Review.
-
Ephaptic communication in the vertebrate retina.Front Hum Neurosci. 2013 Sep 23;7:612. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00612. Front Hum Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24068997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for a retinal progenitor cell in the postnatal and adult mouse.Stem Cell Res. 2017 Aug;23:20-32. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2017.06.010. Epub 2017 Jun 24. Stem Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28672156 Free PMC article.
-
Invaginating Presynaptic Terminals in Neuromuscular Junctions, Photoreceptor Terminals, and Other Synapses of Animals.Neuromolecular Med. 2017 Sep;19(2-3):193-240. doi: 10.1007/s12017-017-8445-y. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Neuromolecular Med. 2017. PMID: 28612182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrastructural Characteristics and Synaptic Connectivity of Photoreceptors in the Simplex Retina of Little Skate (Leucoraja erinacea).eNeuro. 2023 Oct 27;10(10):ENEURO.0226-23.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0226-23.2023. Print 2023 Oct. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 37827837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoyama J (2009) Life history and evolution of migration in catadromous eels (Genus Anguilla). Aqua-BioSci Monogr 2: 1–42.
-
- Van Ginneken VJT, Maes GE (2005) The European eel (Anguilla anguilla, Linaeus), its lifecycle, evolution and reproduction: A literature review. Rev in Fish Biol & Fisheries 15: 367–398.
-
- Tesch F- W (1977) Body structure and functions In: Greenwood PH, editor. The Eel Biology and management of anguillid eels. London: Chapman; pp. 68–73.
-
- Rousseau K, Aroua S, Schmitz M, Elie P, Dufour S (2012) Silvering metamorphosis or puberty In: dvan den thillart G, Dufour S, Rankin JC, editors. Spawning mirgation of the european eel. Netherlands: Spinger; pp. 39–63.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

