Executive dysfunction is associated with poorer health-related quality of life in pediatric brain tumor survivors
- PMID: 27033060
- PMCID: PMC4884154
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-016-2113-1
Executive dysfunction is associated with poorer health-related quality of life in pediatric brain tumor survivors
Abstract
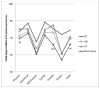
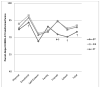
Children with a brain tumor (BT) are at risk for a number of physical and cognitive problems that may lower their health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Executive functioning (EF) and intellectual ability are hypothesized to associate with HRQoL and deficits in these areas may be amenable to interventions. This study aimed to investigate intellectual function, EF, and HRQoL following conformal radiation therapy (CRT) for pediatric BT. Forty-five BT survivors (age 12.68 ± 2.56) treated with CRT participated. Thirty-six siblings of BT patients (age 12.36 ± 2.13) and 33 survivors of non-CNS solid tumors (ST; age 12.18 ± 2.88) were comparison groups. IQ estimate (Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence; WASI), EF ratings (Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function; BRIEF), and HRQoL ratings (KINDL-R) were obtained. BT survivors reported lower overall HRQoL than ST survivors (p = .012). Parents reported lower overall HRQoL for BT survivors than siblings (p = .014). Parent-report on individual areas of HRQoL was higher than self-report for most subscales. IQ and HRQoL ratings were not related (Parent r = .17, p = .27; Child r = .11, p = .49). EF ratings correlated with Parent (r = -.15 to -.73) but not Child HRQoL ratings. Children with BT experienced poorer HRQoL than controls. Children's HRQoL was consistently rated higher by parent- than self-report across all domains. HRQoL was associated with EF, but not with IQ. These findings identify interventions targeting EF (e.g., cognitive rehabilitation, medication) as a possible avenue for improving HRQoL in childhood BT survivors.
Keywords: Executive function; Health-related quality of life; Pediatric brain tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Aran-Filippetti V, Richaud de Minzi MC. A structural analysis of executive functions and socioeconomic status in school-age children: cognitive factors as effect mediators. Journal of Genetic Psychology. 2012;173(4):393–416. - PubMed
-
- Barratt WR. The Barratt Simplified Measure of Social Status. 2006 Retrieved from the Indiana State University website: http://wbarratt.indstate.edu/socialclass/Barratt_Simplified_Measure_of_S....
-
- Benesch M, Spiegl K, Winter A, Passini A, Lackner H, Moser A, Urban C. A scoring system to quantify late effects in children after treatment for medulloblastoma / ependymoma and its correlation with quality of life and neurocognitive functioning. Child's Nervous System. 2009;25(2):173–81. doi: 10.1007/s00381-008-0742-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

