DNA damage regulation and its role in drug-related phenotypes in the malaria parasites
- PMID: 27033103
- PMCID: PMC4817041
- DOI: 10.1038/srep23603
DNA damage regulation and its role in drug-related phenotypes in the malaria parasites
Abstract
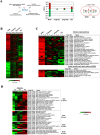
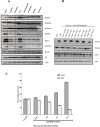
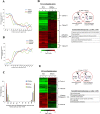
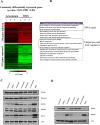
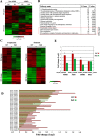
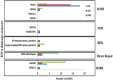
DNA of malaria parasites, Plasmodium falciparum, is subjected to extraordinary high levels of genotoxic insults during its complex life cycle within both the mosquito and human host. Accordingly, most of the components of DNA repair machinery are conserved in the parasite genome. Here, we investigated the genome-wide responses of P. falciparum to DNA damaging agents and provided transcriptional evidence of the existence of the double strand break and excision repair system. We also showed that acetylation at H3K9, H4K8, and H3K56 play a role in the direct and indirect response to DNA damage induced by an alkylating agent, methyl methanesulphonate (MMS). Artemisinin, the first line antimalarial chemotherapeutics elicits a similar response compared to MMS which suggests its activity as a DNA damaging agent. Moreover, in contrast to the wild-type P. falciparum, two strains (Dd2 and W2) previously shown to exhibit a mutator phenotype, fail to induce their DNA repair upon MMS-induced DNA damage. Genome sequencing of the two mutator strains identified point mutations in 18 DNA repair genes which may contribute to this phenomenon.
Figures
References
-
- Ataian Y. & Krebs J. E. Five repair pathways in one context: chromatin modification during DNA repairThis paper is one of a selection of papers published in this Special Issue, entitled 27th International West Coast Chromatin and Chromosome Conference, and has undergone the Journal’s usual peer review process. Biochem Cell Biol 84, 490–494 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Radfar A., Diez A. & Bautista J. M. Chloroquine mediates specific proteome oxidative damage across the erythrocytic cycle of resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Free Radic Biol Med 44, 2034–2042 (2008). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

