Intravesical administration of combined hyaluronic acid (HA) and chondroitin sulfate (CS) for the treatment of female recurrent urinary tract infections: a European multicentre nested case-control study
- PMID: 27033958
- PMCID: PMC4823394
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009669
Intravesical administration of combined hyaluronic acid (HA) and chondroitin sulfate (CS) for the treatment of female recurrent urinary tract infections: a European multicentre nested case-control study
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the clinical effectiveness of the intravesical administration of combined hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate (HA+CS) versus current standard management in adult women with recurrent urinary tract infections (RUTIs).
Setting: A European Union-based multicentre, retrospective nested case-control study.
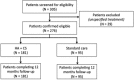
Participants: 276 adult women treated for RUTIs starting from 2009 to 2013.
Interventions: Patients treated with either intravesical administration of HA+CS or standard of care (antimicrobial/immunoactive prophylaxis/probiotics/cranberry).
Primary and secondary outcome measures: The primary outcome was occurrence of bacteriologically confirmed recurrence within 12 months. Secondary outcomes were time to recurrence, total number of recurrences, health-related quality of life and healthcare resource consumption. Crude and adjusted results for unbalanced characteristics are presented.
Results: 181 patients treated with HA+CS and 95 patients treated with standard of care from 7 centres were included. The crude and adjusted ORs (95% CI) for the primary end point were 0.77 (0.46 to 1.28) and 0.51 (0.27 to 0.96), respectively. However, no evidence of improvement in terms of total number of recurrences (incidence rate ratio (95% CI), 0.99 (0.69 to 1.43)) or time to first recurrence was seen (HR (95% CI), 0.99 (0.61 to 1.61)). The benefit of intravesical HA+CS therapy improves when the number of instillations is ≥ 5.
Conclusions: Our results show that bladder instillations of combined HA+CS reduce the risk of bacteriologically confirmed recurrences compared with the current standard management of RUTIs. Total incidence rates and hazard rates were instead non-significantly different between the 2 groups after adjusting for unbalanced factors. In contrast to what happens with antibiotic prophylaxis, the effectiveness of the HA+CS reinstatement therapy improves over time.
Trial registration number: NCT02016118.
Keywords: Antimicrobial Resistance; Hyaluronic acid; chondroitin sulphate.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Recurrent urinary tract infections: prevention of recurrence with intravesical instillations of chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid.].Arch Esp Urol. 2017 Mar;70(2):288-293. Arch Esp Urol. 2017. PMID: 28300032 Spanish.
-
A randomized, open-label, multicenter study of the efficacy and safety of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate versus dimethyl sulfoxide in women with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis.Neurourol Urodyn. 2017 Apr;36(4):1178-1186. doi: 10.1002/nau.23091. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017. PMID: 27654012 Clinical Trial.
-
Is intravesical instillation of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate useful in preventing recurrent bacterial cystitis? A multicenter case control analysis.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Oct;54(5):537-40. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2015.03.005. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2015. PMID: 26522106
-
Part 3: Endoscopic injection versus antibiotic prophylaxis in the reduction of urinary tract infections in patients with vesicoureteral reflux.Curr Med Res Opin. 2007 Sep;23 Suppl 4:S15-20. doi: 10.1185/030079907X226230. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007. PMID: 17931480 Review.
-
Intravesical Therapies for Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Oct 23;16(10):e72175. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72175. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39507191 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate for recurrent urinary tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Urogynecol J. 2018 Jul;29(7):933-942. doi: 10.1007/s00192-017-3508-z. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Int Urogynecol J. 2018. PMID: 29181550 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Deficiencies in the TLR5 Mediated Vaginal Response to Treat Female Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 8;7(1):11039. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10445-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28887442 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic Acid and Chondroitin Sulphate Treatment for Recurrent Severe Urinary Tract Infections due to Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli in a Patient With Multiple Sclerosis: Case Report and Literature Review.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022 May 12;9(7):ofac245. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac245. eCollection 2022 Jul. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35855005 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering S. equi subsp. zooepidemicus towards concurrent production of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin biopolymers of biomedical interest.AMB Express. 2017 Dec;7(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13568-017-0364-7. Epub 2017 Mar 14. AMB Express. 2017. PMID: 28293868 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous production of chondroitin.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2022 Feb 10;33:e00710. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2022.e00710. eCollection 2022 Mar. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2022. PMID: 35242620 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical