Liang-Ge-San, a classic traditional Chinese medicine formula, protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway
- PMID: 27034013
- PMCID: PMC5008280
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8452
Liang-Ge-San, a classic traditional Chinese medicine formula, protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway
Abstract
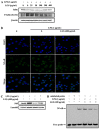
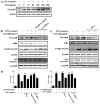
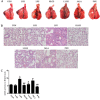
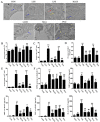
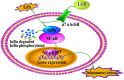
Liang-Ge-San (LGS) is a classic formula in traditional Chinese medicine, which is widely used to treat acute lung injury (ALI), pharyngitis and amygdalitis in clinic. However, the underlying mechanisms remain poorly defined. In this study, we discovered that LGS exerted potent anti-inflammatory effects in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation. We found that LGS significantly depressed the production of IL-6 and TNF-α in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. The degradation and phosphorylation of IκBα and the nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 were also inhibited. Moreover, LGS activated α7 nicotinic cholinergic receptor (α7nAchR). The blockage of α7nAchR by selective inhibitor methyllycaconitine (MLA) or α7nAchR siRNA attenuated the inhibitory effects of LGS on IκBα, NF-κB p65, IL-6 and TNF-α. Critically, LGS significantly inhibited inflammation in LPS-induced ALI rats through the activation of NF-κB signaling pathway. However, these protective effects could be counteracted by the treatment of MLA. Taken together, we first demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects of LGS both in vitro and in vivo through cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. The study provides a rationale for the clinical application of LGS as an anti-inflammatory agent and supports the critical role of cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in inflammation.
Keywords: Immune response; Immunity; Immunology and Microbiology Section; Liang-Ge-San; NF-κB; inflammation; α7 nicotinic cholinergic receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were identified by any of the authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
3-Dehydroandrographolide protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Dec;158:305-317. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.10.034. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30391477
-
Liang-Ge-San, a classic traditional Chinese medicine formula, attenuates acute inflammation in zebrafish and RAW 264.7 cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Mar 1;249:112427. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112427. Epub 2019 Nov 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31778782
-
Liang-Ge-San protects against viral infection-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting α7nAChR-mediated mitophagy.Phytomedicine. 2024 Dec;135:156231. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156231. Epub 2024 Nov 10. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39566410
-
Cholinergic modulation of the immune system presents new approaches for treating inflammation.Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Nov;179:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 18. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28529069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of α7nAChR-Mediated Cholinergic Anti-inflammatory Pathway in Immune Cells.Inflammation. 2021 Jun;44(3):821-834. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01396-6. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33405021 Review.
Cited by
-
Liang-Ge-San: a classic traditional Chinese medicine formula, attenuates acute inflammation via targeting GSK3β.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 29;14:1181319. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1181319. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37456759 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine for Viral Pneumonia Therapy: Pharmacological Basis and Mechanistic Insights.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jan 6;21(3):989-1013. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.105086. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39897040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emodin and baicalein inhibit sodium taurocholate-induced vacuole formation in pancreatic acinar cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jan 7;24(1):35-45. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i1.35. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29358880 Free PMC article.
-
α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist attenuates the cerebral injury in a rat model of cardiopulmonary bypass by activating the Akt/GSK3β pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Dec;16(6):7979-7986. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7600. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28944927 Free PMC article.
-
Liang-Ge-San Decoction Ameliorates Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome via Suppressing p38MAPK-NF-κ B Signaling Pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2025 Jul;31(7):613-623. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3769-6. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Chin J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 39636495
References
-
- Tracey KJ, Beutler B, Lowry SF, Merryweather J, Wolpe S, Milsark IW, Hariri RJ, Fahey TR, Zentella A, Albert JD, Et A. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986;234:470–474. - PubMed
-
- Tracey KJ, Fong Y, Hesse DG, Manogue KR, Lee AT, Kuo GC, Lowry SF, Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987;330:662–664. - PubMed
-
- Rubenfeld GD, Herridge MS. Epidemiology and outcomes of acute lung injury. Chest. 2007;131:554–562. - PubMed
-
- Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW, Tracey KJ. Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature. 2000;405:458–462. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Yu M, Ochani M, Amella CA, Tanovic M, Susarla S, Li JH, Wang H, Yang H, Ulloa L, Al-Abed Y, Czura CJ, Tracey KJ. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature. 2003;421:384–388. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

