Insulin Signaling and Heart Failure
- PMID: 27034277
- PMCID: PMC4833475
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.306206
Insulin Signaling and Heart Failure
Abstract
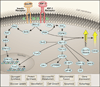
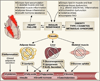
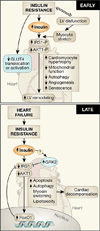
Heart failure is associated with generalized insulin resistance. Moreover, insulin-resistant states such as type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity increases the risk of heart failure even after adjusting for traditional risk factors. Insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes mellitus alters the systemic and neurohumoral milieu, leading to changes in metabolism and signaling pathways in the heart that may contribute to myocardial dysfunction. In addition, changes in insulin signaling within cardiomyocytes develop in the failing heart. The changes range from activation of proximal insulin signaling pathways that may contribute to adverse left ventricular remodeling and mitochondrial dysfunction to repression of distal elements of insulin signaling pathways such as forkhead box O transcriptional signaling or glucose transport, which may also impair cardiac metabolism, structure, and function. This article will review the complexities of insulin signaling within the myocardium and ways in which these pathways are altered in heart failure or in conditions associated with generalized insulin resistance. The implications of these changes for therapeutic approaches to treating or preventing heart failure will be discussed.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; heart failure; insulin receptor; insulin resistance; myocardium.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Norheim OF, Jha P, Admasu K, Godal T, Hum RJ, Kruk ME, Gomez-Dantes O, Mathers CD, Pan H, Sepulveda J, Suraweera W, Verguet S, Woldemariam AT, Yamey G, Jamison DT, Peto R. Avoiding 40% of the premature deaths in each country, 2010–30: Review of national mortality trends to help quantify the un sustainable development goal for health. Lancet. 2015;385:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Magid D, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, Moy CS, Mussolino ME, Nichol G, Paynter NP, Schreiner PJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB American Heart Association Statistics C, Stroke Statistics S. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2013 update: A report from the american heart association. Circulation. 2013;127:e6–e245. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich PA, Trogdon JG, Khavjou OA, Butler J, Dracup K, Ezekowitz MD, Finkelstein EA, Hong Y, Johnston SC, Khera A, Lloyd-Jones DM, Nelson SA, Nichol G, Orenstein D, Wilson PW, Woo YJ American Heart Association Advocacy Coordinating C, Stroke C Council on Cardiovascular R, Intervention, Council on Clinical C , Council on E, Prevention, Council on A, Thrombosis, Vascular B Council on C Critical C Perioperative Resuscitation Council on Cardiovascular N, Council on the Kidney in Cardiovascular D, Council on Cardiovascular S, Anesthesia, Interdisciplinary Council on Quality of C, Outcomes R. Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the united states: A policy statement from the american heart association. Circulation. 2011;123:933–944. - PubMed
-
- Lorenz K, Stathopoulou K, Schmid E, Eder P, Cuello F. Heart failure-specific changes in protein kinase signalling. Pflugers Archiv : European journal of physiology. 2014;466:1151–1162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01HL10837/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL73167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK092065/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21DK073590/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL127764/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL12357/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL108379/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK092065/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK073590/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL087947/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112413/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070070/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

