The Dual Function of Reactive Oxygen/Nitrogen Species in Bioenergetics and Cell Death: The Role of ATP Synthase
- PMID: 27034734
- PMCID: PMC4806282
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/3869610
The Dual Function of Reactive Oxygen/Nitrogen Species in Bioenergetics and Cell Death: The Role of ATP Synthase
Abstract
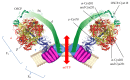
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) targeting mitochondria are major causative factors in disease pathogenesis. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore (PTP) is a mega-channel modulated by calcium and ROS/RNS modifications and it has been described to play a crucial role in many pathophysiological events since prolonged channel opening causes cell death. The recent identification that dimers of ATP synthase form the PTP and the fact that posttranslational modifications caused by ROS/RNS also affect cellular bioenergetics through the modulation of ATP synthase catalysis reveal a dual function of these modifications in the cells. Here, we describe mitochondria as a major site of production and as a target of ROS/RNS and discuss the pathophysiological conditions in which oxidative and nitrosative modifications modulate the catalytic and pore-forming activities of ATP synthase.
Figures

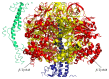
Similar articles
-
The Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore and ATP Synthase.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;240:21-46. doi: 10.1007/164_2016_5. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27590224 Free PMC article.
-
Two mutations in mitochondrial ATP6 gene of ATP synthase, related to human cancer, affect ROS, calcium homeostasis and mitochondrial permeability transition in yeast.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018 Jan;1865(1):117-131. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 28986220
-
The H(+)-ATP synthase: a gate to ROS-mediated cell death or cell survival.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jul;1837(7):1099-112. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2014.03.010. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24685430 Review.
-
Altered FoF1 ATP synthase and susceptibility to mitochondrial permeability transition pore during ischaemia and reperfusion in aging cardiomyocytes.Thromb Haemost. 2015 Mar;113(3):441-51. doi: 10.1160/TH14-10-0901. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 25631625
-
The mitochondrial permeability transition pore and its adaptive responses in tumor cells.Cell Calcium. 2014 Dec;56(6):437-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2014.10.003. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Cell Calcium. 2014. PMID: 25454774 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Inhibition of S-Nitrosoglutathione Reductase Reduces Cardiac Damage Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Apr 2;10(4):555. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040555. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33918310 Free PMC article.
-
N-Methyl-(2S, 4R)-trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline, the major bioactive compound from Sideroxylon obtusifolium, attenuates pilocarpine-induced injury in cultured astrocytes.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022 Nov 4;55:e12381. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2022e12381. eCollection 2022. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2022. PMID: 36350974 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Glutathione in Cellular Redox Homeostasis and Disease Manifestation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 21;25(2):1314. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021314. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluid shear stress enhances proliferation of breast cancer cells via downregulation of the c-subunit of the F1FO ATP synthase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Dec 3;632:173-180. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.09.084. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36209586 Free PMC article.
-
Cultured Rat Hippocampal Neurons Exposed to the Mitochondrial Uncoupler Carbonyl Cyanide Chlorophenylhydrazone Undergo a Rapid, Presenilin-Dependent Change in Neuronal Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 1;25(1):578. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010578. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Le-Quoc K., Le-Quoc D. Crucial role of sulfhydryl groups in the mitochondrial inner membrane structure. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1985;260(12):7422–7428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

