Genotoxicity Studies of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) in the Brain of Mice
- PMID: 27034902
- PMCID: PMC4789523
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/6710840
Genotoxicity Studies of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) in the Brain of Mice
Abstract
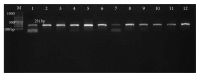
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) are excessively used and represent one of the top five most commonly used nanoparticles worldwide. Recently, various studies referred to their toxic potential on various organs using different treatment route. Male Swiss Webster mice were orally administrated TiO2NPs (500 mg/kg b.w.) daily for five consecutive days and then animals were sacrificed at 24 h, 7 days, or 14 days after the last treatment. The present results report that exposure to TiO2NPs produces mild to moderate changes in the cytoarchitecture of brain tissue in a time dependent manner. Moreover, Comet assay revealed the apoptotic DNA fragmentation, while PCR-SSCP pattern and direct sequencing showed point mutation of Presenilin 1 gene at exon 5, gene linked to inherited forms of the Alzheimer's disease. Therefore, from these findings, the present study concluded that TiO2NPs is genotoxic and mutagenic to brain tissue which in turn might lead to Alzheimer's disease incidence.
Figures

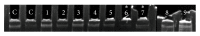



Similar articles
-
Estimation of genotoxicity, apoptosis and oxidative stress induction by TiO2 nanoparticles and acrylamide subacute oral coadministration in mice.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 4;12(1):18648. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23302-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36333451 Free PMC article.
-
Could curcumin ameliorate titanium dioxide nanoparticles effect on the heart? A histopathological, immunohistochemical, and genotoxic study.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Jul;26(21):21556-21564. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05433-2. Epub 2019 May 24. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31127514
-
Estimation of genomic and mitochondrial DNA integrity in the renal tissue of mice administered with acrylamide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 19;13(1):13523. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40676-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37598254 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of TiO2 Nanoparticles Physicochemical Parameters Associated with their Antimicrobial Applications.Indian J Microbiol. 2022 Sep;62(3):338-350. doi: 10.1007/s12088-022-01018-9. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Indian J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35974921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The comet assay with multiple mouse organs: comparison of comet assay results and carcinogenicity with 208 chemicals selected from the IARC monographs and U.S. NTP Carcinogenicity Database.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2000 Nov;30(6):629-799. doi: 10.1080/10408440008951123. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2000. PMID: 11145306 Review.
Cited by
-
Acrylamide coadministration modulates hepatic ROS-mediated apoptotic DNA damage and inflammation induced by TiO2 nanoparticles in mice.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 15;15(1):25444. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10915-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40659659 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-targeted pro-theranostic bi-metallic organo-coordination nanoparticles.Theranostics. 2025 Jan 1;15(4):1205-1220. doi: 10.7150/thno.99863. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 39816680 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of genotoxicity, apoptosis and oxidative stress induction by TiO2 nanoparticles and acrylamide subacute oral coadministration in mice.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 4;12(1):18648. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23302-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36333451 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotoxicity of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 5;18:7183-7204. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S442801. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38076727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoscience and technology as a pivot for sustainable agriculture and its One Health approach awareness.Sci One Health. 2023 Jul 19;2:100020. doi: 10.1016/j.soh.2023.100020. eCollection 2023. Sci One Health. 2023. PMID: 39077037 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schulte P. A., Schubauer-Berigan M. K., Mayweather C., Geraci C. L., Zumwalde R., McKernan J. L. Issues in the development of epidemiologic studies of workers exposed to engineered nanoparticles. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 2009;51(3):323–335. doi: 10.1097/jom.0b013e3181990c2c. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

