Lycopene protects human SH‑SY5Y neuroblastoma cells against hydrogen peroxide‑induced death via inhibition of oxidative stress and mitochondria‑associated apoptotic pathways
- PMID: 27035331
- PMCID: PMC4838073
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5056
Lycopene protects human SH‑SY5Y neuroblastoma cells against hydrogen peroxide‑induced death via inhibition of oxidative stress and mitochondria‑associated apoptotic pathways
Abstract
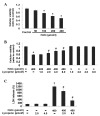
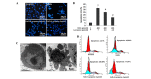
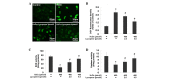
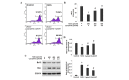
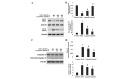
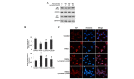
Oxidative stress, which is characterized by excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), is a common pathway that results in neuronal injury or death due to various types of pathological stress. Although lycopene has been identified as a potent antioxidant, its effect on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)‑induced neuronal damage remains unclear. In the present study, pretreatment with lycopene was observed to protect SH‑SY5Y neuroblastoma cells against H2O2‑induced death via inhibition of apoptosis resulting from activation of caspase‑3 and translocation of apoptosis inducing factor (AIF) to the nucleus. Furthermore, the over‑produced ROS, as well as the reduced activities of anti‑oxidative enzymes, superoxide dismutase and catalase, were demonstrated to be alleviated by lycopene. Additionally, lycopene counteracted H2O2‑induced mitochondrial dysfunction, which was evidenced by suppression of mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening, attenuation of the decline of the mitochondrial membrane potential, and inhibition of the increase of Bax and decrease of Bcl‑2 levels within the mitochondria. The release of cytochrome c and AIF from the mitochondria was also reduced. These results indicate that lycopene is a potent neuroprotectant against apoptosis, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, and could be administered to prevent neuronal injury or death.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lycopene protects against trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons by inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.Neurochem Int. 2011 Dec;59(8):1095-103. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.10.005. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Neurochem Int. 2011. PMID: 22032970
-
Crocin protects retinal ganglion cells against H2O2-induced damage through the mitochondrial pathway and activation of NF-κB.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Jan;37(1):225-32. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2418. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26718031
-
Thromboxane A2 receptor antagonist SQ29548 attenuates SH‑SY5Y neuroblastoma cell impairments induced by oxidative stress.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jul;42(1):479-488. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3589. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29620149
-
Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Carotenoids in Neurodegeneration.Molecules. 2020 Jul 29;25(15):3453. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153453. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32751250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress, antioxidant defences and aging.Biofactors. 1998;8(3-4):195-204. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520080305. Biofactors. 1998. PMID: 9914819 Review.
Cited by
-
Lycopene protects against t-BHP-induced neuronal oxidative damage and apoptosis via activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Jun;46(3):3387-3397. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-04801-y. Epub 2019 Apr 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31006097
-
Induction of cell death by pyropheophorbide-α methyl ester-mediated photodynamic therapy in lung cancer A549 cells.Cancer Med. 2017 Mar;6(3):631-639. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1012. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Cancer Med. 2017. PMID: 28181425 Free PMC article.
-
N6-(2-hydroxyethyl)-adenosine from Cordyceps cicadae attenuates hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative toxicity in PC12 cells.Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Oct;34(5):1325-1334. doi: 10.1007/s11011-019-00440-1. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Metab Brain Dis. 2019. PMID: 31197679
-
Deinococcus radiodurans-derived membrane vesicles protect HaCaT cells against H2O2-induced oxidative stress via modulation of MAPK and Nrf2/ARE pathways.Biol Proced Online. 2023 Jun 16;25(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12575-023-00211-4. Biol Proced Online. 2023. PMID: 37328878 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of lycopene on As2O3 induced oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Apr;48(4):3205-3212. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06377-y. Epub 2021 May 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33948854
References
-
- Aliev G, Smith MA, Seyidov D, Neal ML, Lamb BT, Nunomura A, Gasimov EK, Vinters HV, Perry G, LaManna JC, Friedland RP. The role of oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of cerebrovascular lesions in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Pathol. 2002;12:21–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2002.tb00419.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

