Temporal profiles of blood pressure, circulating nitric oxide, and adrenomedullin as predictors of clinical outcome in acute ischemic stroke patients
- PMID: 27035412
- PMCID: PMC4838158
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5001
Temporal profiles of blood pressure, circulating nitric oxide, and adrenomedullin as predictors of clinical outcome in acute ischemic stroke patients
Abstract
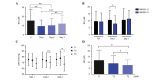
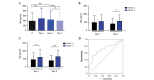
Stroke remains an important health and social challenge. The present study investigated whether blood pressure (BP) parameters and circulating levels of nitric oxide metabolites (NOx) and adrenomedullin (AM) may predict clinical outcomes of stroke. Patients (n=76) diagnosed with acute ischemic stroke were admitted to the stroke unit and clinical history data and monitored parameters were recorded. Blood plasma was collected at days 1, 2, and 7 to measure NOx and AM levels. Infarct volume, neurological severity [on the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS)], and functional prognosis (on the Rankin scale) were measured as clinical outcomes. Patients with higher BP had more severe symptoms (NIHSS >3; P<0.01) and BP variability predicted neurological severity and growth of infarct volume. NOx values were significantly lower in stroke patients than in healthy controls (P<0.01). An increase in NOx levels from day 1 to day 2 was beneficial for the patients as measured by NIHSS at 7 days and 3 months, and by Rankin at 3 months [odds ratio (OR), 0.91] whereas a steep increase from day 2 to day 7 was detrimental and associated with an increase in infarct volume (OR, 35.3). AM levels were significantly higher in patients at day 1 and 2 than in healthy individuals (P<0.01) and these levels returned to normal at day 7. Patients with high AM levels at day 2 had significantly higher NIHSS scores measured at day 1 (P<0.05) and 7 (P<0.01). A receiving operating characteristic curve analysis identified that AM levels at day 2 of >522.13 pg/ml predicted increased neurological severity at day 7 (area under the curve=0.721). Multivariate logistic regression indicated that AM levels at day 2 predicted increased neurological severity at 7 days and at 3 months. BP parameters and changing levels for NOx and AM predicted long‑term clinical outcomes as measured by infarct volume, neurological severity scale, and functional prognosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adrenomedullin Is a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021 Jun 11;43(1):324-334. doi: 10.3390/cimb43010027. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34208106 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma adrenomedullin levels are associated with long-term outcomes of acute ischemic stroke.Peptides. 2014 Feb;52:44-8. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2013.11.025. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Peptides. 2014. PMID: 24333654 Clinical Trial.
-
J-shaped association between serum glucose and functional outcome in acute ischemic stroke.Stroke. 2010 Oct;41(10):2366-70. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.592170. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Stroke. 2010. PMID: 20724712
-
Adrenomedullin in pulmonary hypertension.Dan Med J. 2024 Nov 15;71(12):A07240498. doi: 10.61409/A07240498. Dan Med J. 2024. PMID: 39749558 Review.
-
Cerebral and systemic pathophysiological responses to acute stroke.Age Ageing. 2000 May;29(3):197-202. doi: 10.1093/ageing/29.3.197. Age Ageing. 2000. PMID: 10855898 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Effect of Hypokalemia on Functional Outcome at 3 Months Post-Stroke Among First-Ever Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Jun 10;23:2825-2832. doi: 10.12659/msm.902464. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28600907 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of very early rehabilitation for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 22;15:1423517. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1423517. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39502386 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenomedullin: A vasoactive agent for sporadic and hereditary vascular cognitive impairment.Cereb Circ Cogn Behav. 2021 Mar 4;2:100007. doi: 10.1016/j.cccb.2021.100007. eCollection 2021. Cereb Circ Cogn Behav. 2021. PMID: 36324729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydroxytyrosol, a Promising Supplement in the Management of Human Stroke: An Exploratory Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 27;25(9):4799. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094799. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732018 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenomedullin Is a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021 Jun 11;43(1):324-334. doi: 10.3390/cimb43010027. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34208106 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

