The cyclic AMP signaling pathway: Exploring targets for successful drug discovery (Review)
- PMID: 27035868
- PMCID: PMC4838136
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5005
The cyclic AMP signaling pathway: Exploring targets for successful drug discovery (Review)
Abstract
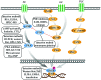
During development of disease, complex intracellular signaling pathways regulate an intricate series of events, including resistance to external toxins, the secretion of cytokines and the production of pathological phenomena. Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) is a nucleotide that acts as a key second messenger in numerous signal transduction pathways. cAMP regulates various cellular functions, including cell growth and differentiation, gene transcription and protein expression. This review aimed to provide an understanding of the effects of the cAMP signaling pathway and the associated factors on disease occurrence and development by examining the information from a new perspective. These novel insights aimed to promote the development of novel therapeutic approaches and aid in the development of new drugs.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

