Staphylococcus aureus Transcriptome Architecture: From Laboratory to Infection-Mimicking Conditions
- PMID: 27035918
- PMCID: PMC4818034
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005962
Staphylococcus aureus Transcriptome Architecture: From Laboratory to Infection-Mimicking Conditions
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is a major pathogen that colonizes about 20% of the human population. Intriguingly, this Gram-positive bacterium can survive and thrive under a wide range of different conditions, both inside and outside the human body. Here, we investigated the transcriptional adaptation of S. aureus HG001, a derivative of strain NCTC 8325, across experimental conditions ranging from optimal growth in vitro to intracellular growth in host cells. These data establish an extensive repertoire of transcription units and non-coding RNAs, a classification of 1412 promoters according to their dependence on the RNA polymerase sigma factors SigA or SigB, and allow identification of new potential targets for several known transcription factors. In particular, this study revealed a relatively low abundance of antisense RNAs in S. aureus, where they overlap only 6% of the coding genes, and only 19 antisense RNAs not co-transcribed with other genes were found. Promoter analysis and comparison with Bacillus subtilis links the small number of antisense RNAs to a less profound impact of alternative sigma factors in S. aureus. Furthermore, we revealed that Rho-dependent transcription termination suppresses pervasive antisense transcription, presumably originating from abundant spurious transcription initiation in this A+T-rich genome, which would otherwise affect expression of the overlapped genes. In summary, our study provides genome-wide information on transcriptional regulation and non-coding RNAs in S. aureus as well as new insights into the biological function of Rho and the implications of spurious transcription in bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

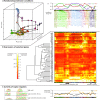
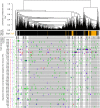


Similar articles
-
The sigmaB regulon in Staphylococcus aureus and its regulation.Int J Med Microbiol. 2006 Aug;296(4-5):237-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.11.011. Epub 2006 Apr 27. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16644280
-
The alternative sigma factor B modulates virulence gene expression in a murine Staphylococcus aureus infection model but does not influence kidney gene expression pattern of the host.Int J Med Microbiol. 2012 Jan;302(1):33-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2011.09.013. Epub 2011 Oct 22. Int J Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22019488
-
The influence of SaeRS and σ(B) on the expression of superantigens in different Staphylococcus aureus isolates.Int J Med Microbiol. 2011 Aug;301(6):488-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2011.01.003. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Int J Med Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21470910
-
Genome-wide determination of transcription start sites reveals new insights into promoter structures in the actinomycete Corynebacterium glutamicum.J Biotechnol. 2017 Sep 10;257:99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 Apr 13. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28412515
-
The importance of regulatory RNAs in Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Genet Evol. 2014 Jan;21:616-26. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.11.016. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Infect Genet Evol. 2014. PMID: 24291227 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome architecture and regulation at environmental transitions in flavobacteria: the case of an important fish pathogen.ISME Commun. 2021 Jul 7;1(1):33. doi: 10.1038/s43705-021-00029-9. ISME Commun. 2021. PMID: 36739365 Free PMC article.
-
RelQ Mediates the Expression of β-Lactam Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Front Microbiol. 2019 Mar 11;10:339. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00339. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30915038 Free PMC article.
-
A global Staphylococcus aureus proteome resource applied to the in vivo characterization of host-pathogen interactions.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 8;7(1):9718. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10059-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28887440 Free PMC article.
-
Termination factor Rho: From the control of pervasive transcription to cell fate determination in Bacillus subtilis.PLoS Genet. 2017 Jul 19;13(7):e1006909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006909. eCollection 2017 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28723971 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible expression of (pp)pGpp synthetases in Staphylococcus aureus is associated with activation of stress response genes.PLoS Genet. 2020 Dec 30;16(12):e1009282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009282. eCollection 2020 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 33378356 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

