Defects in lysosomal maturation facilitate the activation of innate sensors in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 27035940
- PMCID: PMC4839468
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1513943113
Defects in lysosomal maturation facilitate the activation of innate sensors in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
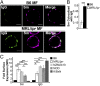
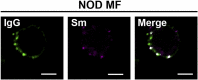
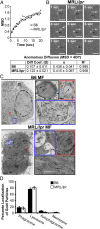
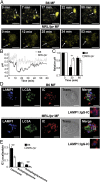
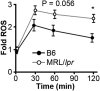
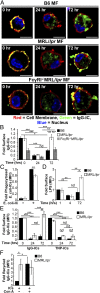
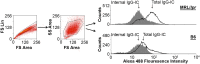
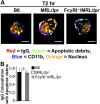
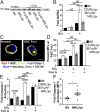
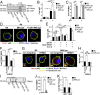
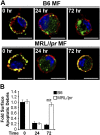
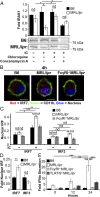
Defects in clearing apoptotic debris disrupt tissue and immunological homeostasis, leading to autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Herein, we report that macrophages from lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice have impaired lysosomal maturation, resulting in heightened ROS production and attenuated lysosomal acidification. Impaired lysosomal maturation diminishes the ability of lysosomes to degrade apoptotic debris contained within IgG-immune complexes (IgG-ICs) and promotes recycling and the accumulation of nuclear self-antigens at the membrane 72 h after internalization. Diminished degradation of IgG-ICs prolongs the intracellular residency of nucleic acids, leading to the activation of Toll-like receptors. It also promotes phagosomal membrane permeabilization, allowing dsDNA and IgG to leak into the cytosol and activate AIM2 and TRIM21. Collectively, these events promote the accumulation of nuclear antigens and activate innate sensors that drive IFNα production and heightened cell death. These data identify a previously unidentified defect in lysosomal maturation that provides a mechanism for the chronic activation of intracellular innate sensors in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Keywords: AIM2; Fc gamma receptors; TRIM21; lysosomal acidification; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apoptotic Debris Accumulates on Hematopoietic Cells and Promotes Disease in Murine and Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.J Immunol. 2016 May 15;196(10):4030-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500418. Epub 2016 Apr 8. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27059595 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Toll-like receptor-7 (TLR-7) or TLR-7 plus TLR-9 attenuates glomerulonephritis and lung injury in experimental lupus.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007 Jun;18(6):1721-31. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006101162. Epub 2007 Apr 25. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17460144
-
Lupus-Associated Immune Complexes Activate Human Neutrophils in an FcγRIIA-Dependent but TLR-Independent Response.J Immunol. 2019 Feb 1;202(3):675-683. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800300. Epub 2019 Jan 4. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30610165 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptors in systemic lupus erythematosus; prospects for therapeutic intervention.Autoimmun Rev. 2009 Jan;8(3):204-8. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2008.07.046. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Autoimmun Rev. 2009. PMID: 18722558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptors and activation of autoreactive B cells.Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2003;6:105-22. doi: 10.1159/000066858. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2003. PMID: 12408049 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Cytoplasmic DNA and AIM2 inflammasome in RA: where they come from and where they go?Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 10;15:1343325. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343325. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39450183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis in lupus mice identifies Coronin-1A as a potential biomarker for lupus nephritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Jun 18;22(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02236-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32552896 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxychloroquine and COVID-19: a Rheumatologist's Take on the Lessons Learned.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021 Jan 21;21(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s11882-020-00983-9. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2021. PMID: 33475900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of cxorf21 Provides Molecular Insight Into Female-Bias Immune Response in SLE Pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 21;10:2160. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02160. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31695690 Free PMC article.
-
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein restricts cGAS/STING activation by dsDNA immune complexes.JCI Insight. 2020 Sep 3;5(17):e132857. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.132857. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32721945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klemperer P. The pathogenesis of lupus erythematosus and allied conditions. Ann Intern Med. 1948;28(1):1–11. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn A, et al. Accumulation of apoptotic cells in the epidermis of patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus after ultraviolet irradiation. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(3):939–950. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

